Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Foreign Exchange Hedging Strategies at General Motors: Competitive Exposures Case Solution
World’s largest automaker and the sales leader, General Motors was carrying out its manufacturing in thirty countries while selling its finished vehicles in approximately two hundred countries. With a market share of 15.1%, GM was competing with various other companies which have differing home currencies. This phenomenon of competition with other corporations, especially the Japanese companies, which has greater part of cost structure denominated in Yen gave rise to the currency risk exposure, due to fluctuations in the movement of Yen against the dollar. These real risks to the company had not been accounted for before; therefore, it had become essential to estimate the risk magnitude and devise the risk management policy.
Following questions are answered in this case study solution:
-
Why is GM worried about the value of the yen? What types of currency exposures does GM face?
-
Does GM’s corporate hedging policy described in the case seem sensible?
-
How would you estimate volatility in the value of the yen?
-
Using one or more of the alternatives in question 3, make your own estimate of the standard deviation of the yen against the dollar at various horizons relevant to GM.
-
How important is GM’s competitive exposure to the yen?
-
How would estimate a value exposure for GM from the case information about competitive interactions with Japanese firms?
-
What other less information-intensive methods might allow you to assess GM’s competitive exposure? Would these methods be useful for assessing competitive exposures for other firms? How would you implement such a method?
-
How would you recommend GM manage its operating or competitive exposures?
Foreign Exchange Hedging Strategies at General Motors Competitive Exposures Case Analysis
1. Why is GM worried about the value of the yen? What type of currency exposure does the GM face?
Observing the historical trend in the exhibit 4, Eric Feldstein, the vice president and the treasurer of the company anticipated the long term consequences of the fluctuations in the Japanese yen against the U.S. dollar. His position was valid as the situation was worrisome because the Japanese Yen was depreciating constantly against the U.S. dollar during the previous years. Hence, the depreciation value of Yen would result in the decreased cost as compared to companies operating in US; therefore, these cost savings would be translated into the cost benefit for the end consumer by lowering down the final prices of the autos. Ultimately, the market share of the Japanese companies would experience growth against the General Motors. The economic consequence of the depreciating yen was anticipated by the previously estimated decreased operating profits when the Yen appreciated previously from 117 to 107 during the year 2000.
Furthermore, the competitive Yen exposure was affecting the GM’s overall exposure because the company was already facing various other currency risk exposures. For the instance,
-
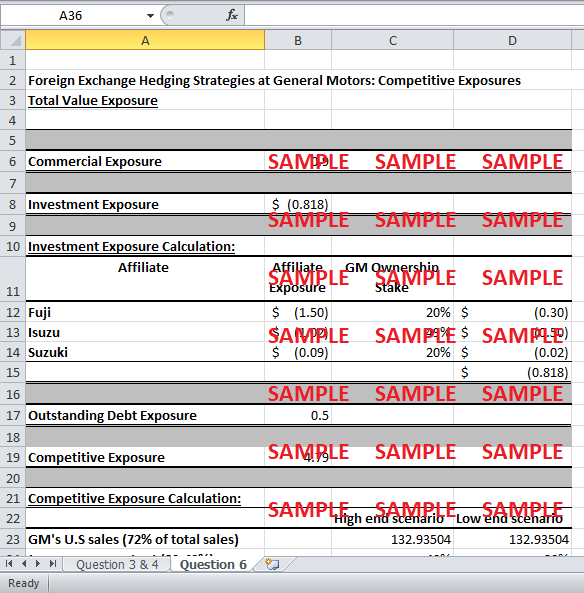
Commercial Exposure which amounted for $ 900 Million.
-
Investment Exposure due to the investment in Fuji, Isuzu and Suzuki.
-
Financing Exposure resulting from the yen denominated bonds worth $500 Million.
2. Does GM’s corporate hedging policy described in the case seem sensible?
Based on the parameters of the company and the key objectives of the company risk management policy, the appropriateness of the GM’s corporate hedging policy can be analyzed. Generally, corporate hedging serves the purpose of maximizing value through risk management. However, GM has its own specific objectives such as to decrease the volatility of the cash flows and earnings along with the limited time and cost allocation to this particular strategy. Therefore, in order to serve the purpose the company adopted passive hedging policy to manage foreign exchange risk, regionally. Based on the fact that, 72% of the GM’s sales were regional i.e. in North America; therefore, managing risk regionally to assure consistency with the company operations seems sensible. Moreover, the company has not yet experienced any significant exposure to yen from any foreign exchange transaction; therefore, it is wiser to adopt the passive strategy. This argument is further validated by the results of an internal study that the active management of the foreign exchange exposure does not outperform the passive management of risk. Besides, the 50% of the foreign exchange exposure is hedged, which seems appropriate as the company has not experienced any substantial exposure yet and even if the market does not behave in favor of GM 50% is still hedged, and if it operates in favor of the company; not only GM will enjoy the benefits but also it will be able to save those funds which could have been used for the rest of the 50% FX exposure.
3. How would you estimate volatility in the value of the yen?
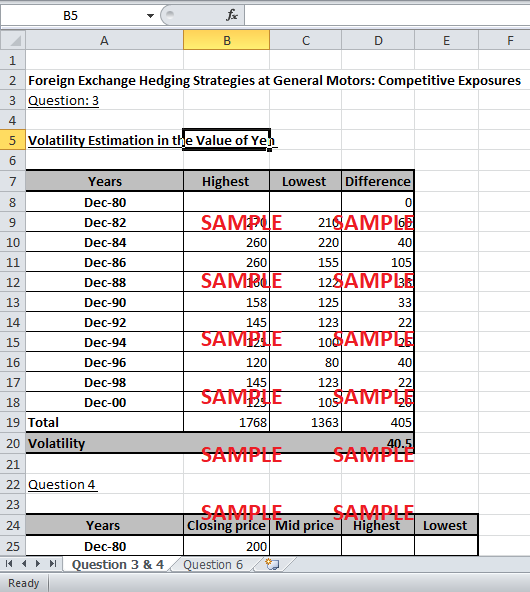
In accordance with the given case, volatility is the measure of uncertainty in the exchange rate of yen against the dollar. The required estimate of volatility is calculated with the help of exhibit 4. The closing prices of the 2 year period are given from December 1980 to December 2000. Within each 2 year period range highest and lowest rate is estimated through the values given on the y axis. The difference is taken between the highest and lowest rates of each period. Average of the sum of the difference is the volatility of the exchange rate. The calculations are displayed in the exhibits.
4. Using one or more alternatives in the question 3, make your estimate of the standard deviation of the yen against the dollar at various horizons relevant to GM?
The uncertainty around the mean exchange rate of yen against dollar can also be calculated through the standard deviation. The greater the standard deviation the greater will be the volatility. Therefore, the standard deviation of the closing price, the mid-price and the highest and lowest rate is calculated. The average of the sum of all the values is the estimated standard deviation which has incorporated the rates at various time periods i.e. the closing period; middle period and period of highest and lowest rate altogether.
5. How important is the GM’s competitive exposure to Yen?
GM’s competitive exposure is significant according to the facts stated in the case. One of the most important consequences of the yen depreciation is that for one yen depreciation against the dollar, the operating profits of the Japanese company increased by more than $0.4 Billion. Moreover, the significance of competitive exposure is further supported by the research estimates which stated that at 110/$, yen the Japanese companies were unprofitable as compared to 120/$ when Japanese firm’s grew profitable.
Furthermore, based on the information provided in case, the competitive exposure to Yen is calculated for both the high end and low end scenarios. The calculations are shown in the exhibits; however, it is observed that for 3.6% decline in the prices of the Japanese firms, GM faces the threat of losing 7.2% market share. Hence, the results indicate that the substantial consideration is needed to be given by the management to the competitive exposures to Yen.
6. How would you estimate a value exposure for GM from the case information about competitive interactions with Japanese firms?
The value exposure of GM is comprised of the commercial, investment, outstanding debt and the competitive exposure. Therefore, the commercial exposure of around $900 million is taken in to account while calculating the total exposure. Moreover, the investment exposure is calculated by the summation of the weighted exposure of the GM due to investment in Fuji, Isuzu, and Suzuki. The data given in exhibit 5 formed the basis of the calculated $0.818 Billion investment exposure in the excel exhibits.
Besides the outstanding debt exposure is considered to be the $500 Million bonds denominated in yen. However, the competitive exposure has to be quantified by considering that the Japanese content in each car is 20 - 40% while the cost savings translated into the lowering down of sticker prices is 15 - 45%. Moreover, the yen is assumed to be depreciated at 20%. Therefore, in the high end scenario the decline in prices is 3.6% by multiplying the 40% Japanese content with the 45% costs savings and 20% depreciation in yen. Similarly, the low end scenario declining price is calculated.
Lastly, the summation of the four exposures is calculated as the estimated value exposure for GM.
7. What other less information-intensive methods might allow you to assess GM’s competitive exposure? Would these methods be useful for assessing competitive exposures for other firms? How would you implement such a method?
In order to quantify GM’s exposures to Yen, the less information intensive method could be regression of the financials of GM with the Yen Index. This approach will establish a correlation between the changes in cash flow with one unit change in Yen. In order to implement this method, financials of the previous years can be obtained followed by the calculation of cash flow statement which will be undergone regression with the Yen index.
8. How would you recommend GM manage its operating or competitive exposures?
GM can manage its operating and competitive exposures through a number of following ways:
-
Enhancing investment in affiliates
GM can increase its investment in the affiliates as they are already providing hedge against the Yen depreciation. It will be feasible because it will not require any change in the company operations; however, there is a limit and target to which GM’s investment in affiliates is feasible in terms of benefits gained.
-
Pricing Strategy
GM can price its products indexed to Yen. Therefore, as the yen depreciates the price of the GM automotive will also reduce; however, it will be a cause of concern if the yen appreciates as the exchange rates are volatile.
Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Get Instant Access to This Case Solution for Only $19
Standard Price
$25
Save $6 on your purchase
-$6
Amount to Pay
$19
Different Requirements? Order a Custom Solution
Calculate the Price
Related Case Solutions
- Foreign Exchange Hedging Strategies at General Motors- Transactional and Translational Exposures Case Solution
- Founder-CEO Succession at Wily Technology Case Solution
- Four Seasons Goes to Paris:53 Properties, 24 Countries, 1 Philosophy Case Solution
- Four Star Industries Singapore- Matching Supply with Demand Case Solution
- Frasier (A) Case Solution
Get More Out of This
Our essay writing services are the best in the world. If you are in search of a professional essay writer, place your order on our website.