Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Caribbean Internet Cafe Case Solution
David Grant, an MBA student, wants to open Caribbean Internet Café (CIC) in Kingston, Jamaica after he graduates. He thought this was a good business opportunity as Jamaica had reasonable internet users but low internet accessibility. As he was opening the first internet café, he would have a first mover advantage. During his vacation, he estimated the start-up costs, fixed costs and variable costs of operating CIC. Being a former employee at Jamaica Telecommunications Limited (JTL), he approached JTL to invest in his business. JTL proposed to invest $500,000 equity and provide $1,250,000 loan for 10% interest. Grant, now, has to determine the profitability of the proposed business and decide to proceed with the venture or not.
Following questions are answered in this case study solution:
-
What managerial issues should David Grant consider before starting the Caribbean Internet Café?
-
Define the fixed, variable and start-up costs in this case.
-
What will be the costs for the very first customer?
-
What is the contribution margin per customer?
-
How many customer visits will CIC need in order for the café to break-even in the first year?
-
How many customer visits will CIC need in order for the café to break-even in year two?
-
Should Grant proceed with the venture?
Caribbean Internet Caf Case Analysis
1. What managerial issues should David Grant consider before starting the Caribbean Internet Café?
There are various managerial issues concerning Grant about the internet café. Firstly, the café has a high startup cost of $1,573,000. Grant would be concerned about recovering the initial investment. Hence, he has to determine whether the benefits are enough to recover the cost and earn additional profit for him.
Other political, economic, social and technological issues will also have a severe impact on the business of CIC. The setting up of the café might be hindered and slowed by bureaucracy and corruption in Jamaica. Similarly, the fluctuation in prices of internet and equipment is also a potential threat for the business. Furthermore, with technological progress, the equipment might become obsolete and lose their value. Also, the improvement in internet accessibility for the population could also cause problems for the café. Another problem for the business might be the low barriers to entry. This might cause new cafes opening nearby. This could lead to price wars, which would sufficiently reduce the return for the business.
However, it is important to note that Grant has certain opportunities to earn high returns. As Jamaica lacks Internet café, CIC will have a first mover advantage. Additionally, the location of the café is ideal to attract maximum customers who require internet usage. Another positive factor for the business is the staff. As the staff would consist of employees and manager with experience in the restaurant industry, CIC will be able to attract and retain customers.
2. Define the fixed, variable and start-up costs in this case.
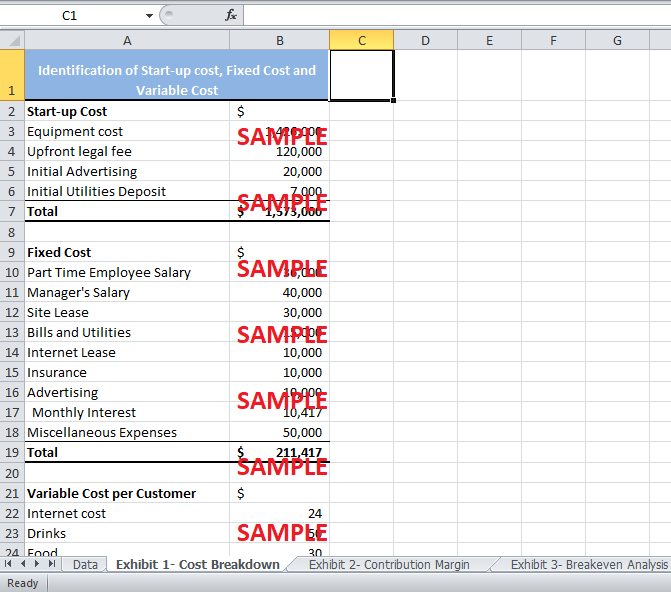
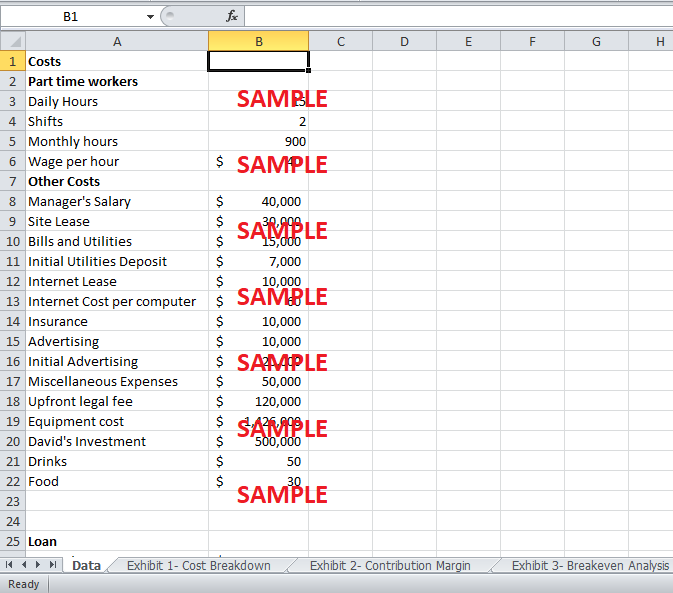
Exhibit 1 shows the division of all the costs under fixed, variable and start-up costs. The start-up costs include all the initial outlay required to set up the Internet café in Jamaica. Grant requires a total initial investment of $1,573,000. This mainly includes the cost of equipments e.g. general equipments, hardware, software, and furniture. The total cost of equipment was $1,426,000. Other start-up costs include upfront legal fee of $120,000, additional advertising of $20,000 and initial utilities deposit of $10,000. Grant must have to invest in all these costs to get his business up and running. These are one-time costs and will be recovered over the three years investment period of the café.
The fixed costs are the costs that are more or less fixed and do not vary with the number of customers in the café. These costs include the salary of manager, the part time wage, the site lease payment, the internet lease payment to JLT, telephone bills and utilities, and Insurance expenses. If Grant accepts JLT’s proposal and take a loan of $1,250,000, he would have additional fixed cost of monthly interest payment on the loan of $10,417. This results in a total monthly fixed cost of $211,417.
Lastly, variable costs are the costs which vary with the level of service provided. This includes the cost of internet usage, drinks and food. It is estimated that forty percent of the customers will visit the café for internet usage. Hence, the $60 internet cost per computer will be $24 per customer. The total variable cost per customer turns out to be $104.
3. What will be the costs for the very first customer?
For the very first customer, the cost will be the total monthly fixed cost plus the variable cost. This would mean a cost of $211,521. As CIC gets more and more customers, the fixed cost is spread over more and more customer. Hence, fixed cost per customer reduces as customers increase. However, the variable cost per customer will remain the same.
4. What is the contribution margin per customer?
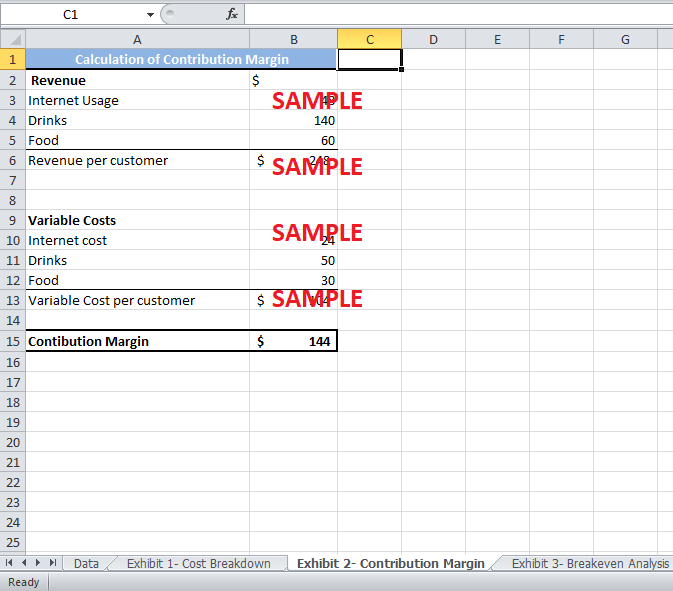
Exhibit 2 shows the calculation for the contribution margin per customer. The revenue from drinks and food would be $140 and $60. The internet usage price per customer is $120 per customer. As it is estimated that 40% of the internet users will come to the café, the average internet revenue per customer would be $48. Therefore, the average revenue per customer would be $248. The variable cost per customer is $104. The contribution margin per customer is calculated to be $144.
5. How many customer visits will CIC need in order for the café to break-even in the first year?
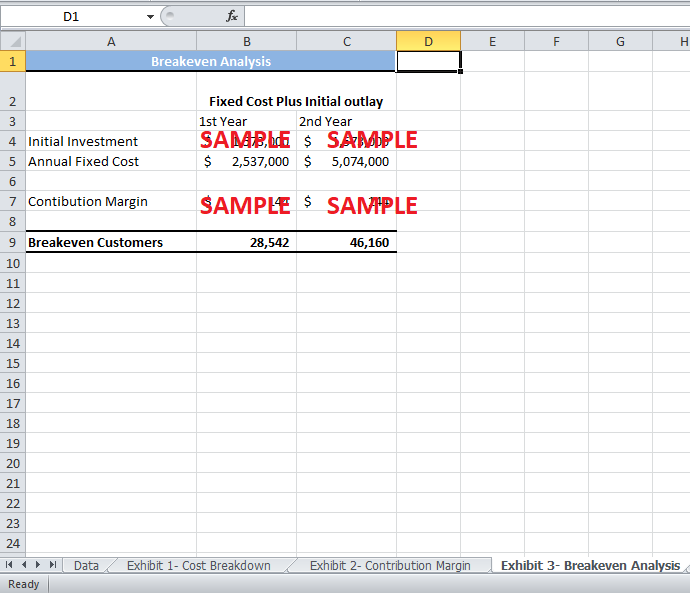
Exhibit 3 shows the number of customer visits required by CIC to breakeven in the first year. The total initial investment, total fixed cost and the contribution margin per customer are used to calculate the breakeven customers. The breakeven number of customer visits is 28,542.
6. How many customer visits will CIC need in order for the café to break-even in year two?
In order to recover the initial investment and meet the fixed costs in year two, CIC would need to have attracted at least 46,160 customer visits in two years of business (Exhibit 3). For CIC, this might be a high target to achieve.
Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Get Instant Access to This Case Solution for Only $19
Standard Price
$25
Save $6 on your purchase
-$6
Amount to Pay
$19
Different Requirements? Order a Custom Solution
Calculate the Price
Related Case Solutions
Get More Out of This
Our essay writing services are the best in the world. If you are in search of a professional essay writer, place your order on our website.