Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Charles River Jazz Festival Case Solution
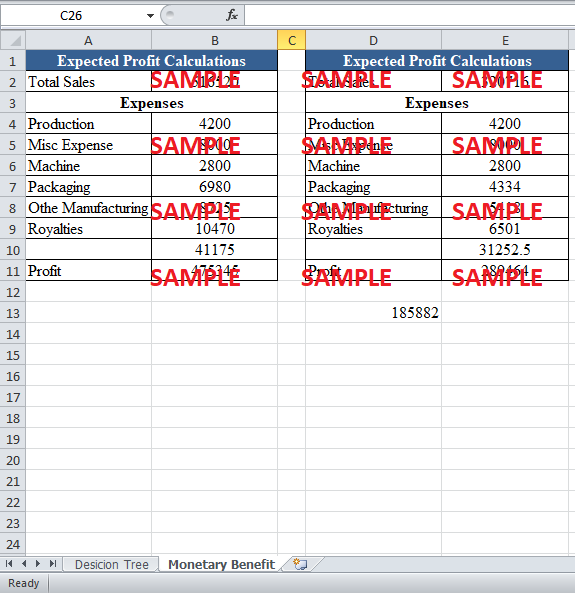
Buzz Ward is concerned about the demand projections for his new business idea for Charles River jazz festival. The projections of probabilities of low and high sales show that in the current scenario, the maximum amount of sales cannot exceed 3490 units. This will be the scenario when the Saturday sales are high. On the other hand, the minimum sales are equal to 2167 units. The maximum and minimum profits are equal to $475345 and $289464 respectively. The maximum expected monetary value is, therefore, equal to $475345. The maximum amount that Buzz can pay for the perfect demand information is equal to $185,882. Additionally, in order to influence the production decisions, the local record distributor has to pay an additional $7.5 per unit to Buzz.
Following questions are answered in this case study solution:
-
Using Buzz's probability estimate, what is the probability that demand for compact disks will be exactly 4,000 compact disks during the festival, i.e., over Saturday and Sunday combined?
-
Draw an appropriate decision tree for Buzz's problem, i.e., to determine how many compact disks CRJF should press on Friday. Be sure to include probabilities and the value of the endpoints.
-
How many CDs should Charles River Jazz Festival press on Friday? Use maximization of Expected Monetary Value as a criterion.
-
What is the Expected Monetary Value of the best plan in Question 3?
-
Suppose that Buzz could obtain information about the demand for CDs prior to committing to the CD project (i.e., before paying any fees to Comco or incurring any of the miscellaneous costs). What is the most he should pay for perfect information about the two-day demand for CDs?
-
Assume for this question only that any unsold compact disks could be sold to a local record distributor. How high a price would record distributor has to pay, per disk, for Buzz to change his production quantity decision?
Charles River Jazz Festival Case Analysis
1. Using Buzz's probability estimate, what is the probability that demand for compact disks will be exactly 4,000 compact disks during the festival, i.e., over Saturday and Sunday combined?
In order to find out the probability of 4000 units, first you have to calculate the projected amount of units at the given probabilities. There are two broad results that can arise. A low demand on Saturday will yield a high subsequent demand on Sunday. On the other hand, a high Saturday demand will yield a high Sunday demand. However, the probability of a high demand on Saturday is quite low. In the case of low Saturday demand, the units demanded will be equal to 1000. Additionally, on Sunday, the subsequent probabilities show that a total of 1500 (1000*.75+3000*.25) Units are demanded. Therefore, the total units demanded in this case are 2500 (1500+1000). Conversely, a high demand on Saturday will provide 3000 units on Saturday. On Sunday, the consequent demand will be 2500 (1000*.25+3000*.75). Hence, the total demand in this case is equal to 5500 (2500+3000). Now, let’s calculate the total amount of units demanded as per the projections. The following formula is used to carry out the relevant calculation.
Total Units demanded = (1500+1000)*.67+ (2500+3000)*.33=3490
The total demanded units are equal to 3490. This is lower than the 4000 units figure. A there are zero chances of sales above 3490; therefore, probability of sales of 4000 is zero.
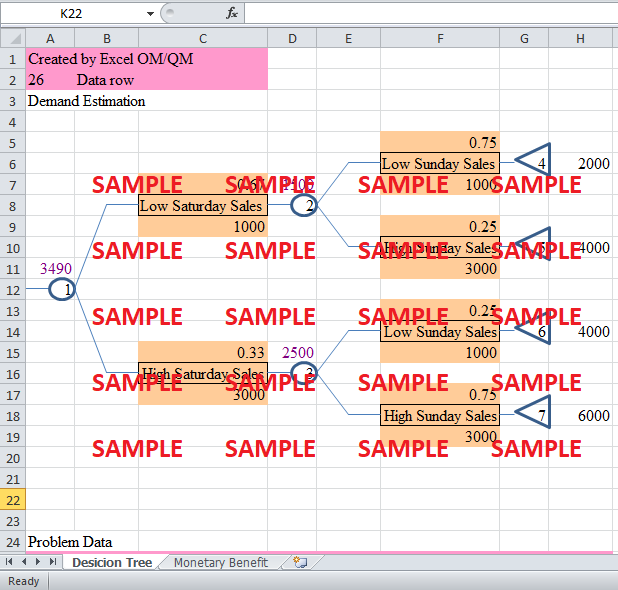
2. Draw an appropriate decision tree for Buzz's problem, i.e., to determine how many compact disks CRJF should press on Friday. Be sure to include probabilities and the value of the endpoints?
Let’s assume that CRJF wants to stick to the higher output of demand. As discussed above, there are two broad scenarios. The chance of every scenario is different, and the probabilities of the subsequent events are also changed. The decision tree will start from the decision node where Buzz is faced with two scenarios, a high demand or a low demand on Saturday. Therefore, there will be two nodes arising from the mother node. The first node will represent high Saturday demand and the other will represent low Saturday demand. Both of these nodes are followed by two nodes each. The low Saturday sales are followed by Low Sunday sales and high Sunday sales scenarios. The probability of these scenarios is 0.75 and 0.25 respectively. The high Saturday sales are followed by exactly the same two nodes, but the probabilities are different. The probability of Low Sunday sales is 0.25, and the probability of high Sunday sales is 0.75. The values of high and low sales in b all of the scenarios are 3000 and 1000 respectively. The under consideration decision tree is listed in the following diagram.
As shown in the mother node, the maximum amounts of sales that can be generated from any combination of scenario are equal to 3490 units. Also, in the case of a low Saturday sales, the Sunday sales will be equal to 1500 units. And so, the total unit sales in the case of low Saturday sales are 2167 units. This is the minimum amount of units that can be demanded in case of the worst demand scenario.
3. How many CDs should Charles River Jazz Festival press on Friday? Use maximization of Expected Monetary Value as a criterion.
The decision of pressing CDs on Friday depends on the selection criterion of Jazz. In the current situation, the relevant criteria are maximization of expected monetary value. In this case, Jazz will be looking forward to the idea of generating maximum unit sales in order to attain high revenue. Therefore, at the mother node, that option will be chosen that yields maximum unit sales. Therefore, Jazz should stick to the decision that is most optimistic. In the current scenario, as described in the above mentioned decision tree, two distinct scenarios are mentioned. The Sunday sales in the first scenario are equal to 1500 units. On the other hand, the second option inculcates 2500 unit sales in it. The low Saturday sales option yields total unit sales of 2167, both for Saturday and Sunday. On the other hand, the high Saturday sales will give way to sales of 3490 units. Therefore, the expected monetary value is maximized at high Saturday sales option. Jazz should press 3490 CDs on Friday to maximize the monetary value.
Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Get Instant Access to This Case Solution for Only $19
Standard Price
$25
Save $6 on your purchase
-$6
Amount to Pay
$19
Different Requirements? Order a Custom Solution
Calculate the Price
Related Case Solutions
Get More Out of This
Our essay writing services are the best in the world. If you are in search of a professional essay writer, place your order on our website.