Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
ENTERTAINMENTNOW.COM Case Solution
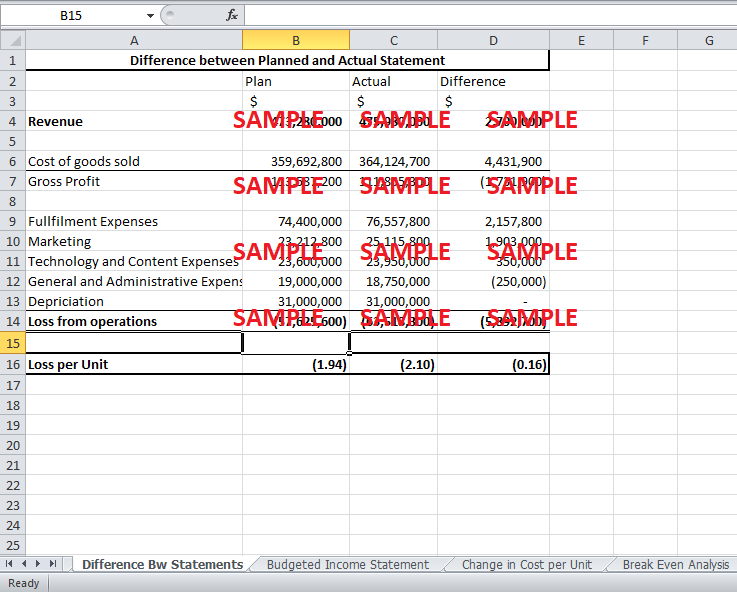
EntertainmentNow.com was a company that offered a large collection of books, music, DVDs, toys and electronics for sale on the company’s website. Although EntertainmentNow.com began by catering to individual customers, it had also begun serving corporate and institutional clients. Over the last few years, the company invested heavily in technology and infrastructure. This led to a net loss for the company. The actual loss per unit of $2.10 was also higher than the planned loss per unit of $1.94. The loss increased despite the rise in sales units and revenue for the company. Hence, a proper financial analysis required to determine the reasons for the increased loss.
Following questions are answered in this case study solution:
-
Conceptually, what factors explain the difference between planned and actual results?
-
Prepare a flexible budget for EntertainmentNow.com for the past year, flexing solely on total actual units sold.
-
Quantify the impact on the net loss per item sold of each factor you noted in Question 1.
-
Assume that technology and content, general and administrative, and depreciation and amortization costs are fixed costs that total $73.7 million annually. Based on EntertainmentNow.com’s current sales revenue, cost of goods sold, fulfillment expenses, and marketing, what is the company’s break-even sales in units? Is this level of sales realistic? Why or why not?
ENTERTAINMENTNOW COM Case Analysis
1. Conceptually, what factors explain the difference between planned and actual results?
EntertainmentNow.com faced problems due to the increased expenditure on technology and infrastructure. When the capital investment was charged to the income statement, it damaged the profits of the business. Thus, conceptually, the higher than expected fixed cost seem like the major reason for increasing loss. The technology and content expenses were higher by $350,000 compared to the planned expenses. However, the general and administrative expenses were less by $250,000 from the budgeted. Hence, there will be more reasons for the discrepancy between the planned and the actual than just a net increase of $100,000 in fixed costs. Exhibit 1 shows all the factors causing the variance between the actual and budgeted loss.
Firstly, the units sold were significantly higher than the budgeted units. The budgeted unit sales were a total 29.76 million, but the actual number sold was around 30.26 million. Higher volume of sales by 0.5 million units is significant to increase the variable expenses. EntertainmentNow.com sold 1 million more books than expected. DVDs, toys and Electronic sales were also greater than expected by 320,000, 150,000 and 30,000, respectively. On the other hand, it sold 1 million less music than expected.
Secondly, the change in the pricing of the products can be a critical reason for the difference. EntertainmentNow.com reduced the price of books, DVDs and Toys by $0.5, $2 and $5 per unit, respectively. Similarly, the firm increased the price of Music and Electronics by $1 and $3 per unit. Hence, these changes in prices over a large volume mean a significant loss in revenue.
Finally, another reason for the difference in budgeted and actual losses was the changes in the variable costs. The cost of goods sold rose from 76% of revenue to 76.5%. Thus, change in cost of goods sold was not only due to the change in revenue but also due to the increase in percentage of revenue attributed to the cost of sales. Similarly, the fulfillment cost also increased from $2.50 per unit to $2.53 per unit. This increase in per unit cost coupled with the increase in sales volume increased fulfillment expenses by $2,157,800. Due to an advertising campaign to attract sales, the marketing cost per unit also increased by $0.05. This increase along with an increase in sales caused marketing expenses to increase by $1,903,000 (Exhibit 2).
Conceptually, as the fixed cost changed slightly, the loss per unit should have decreased with the increase in units sold. However, the loss per unit has increased tremendously.
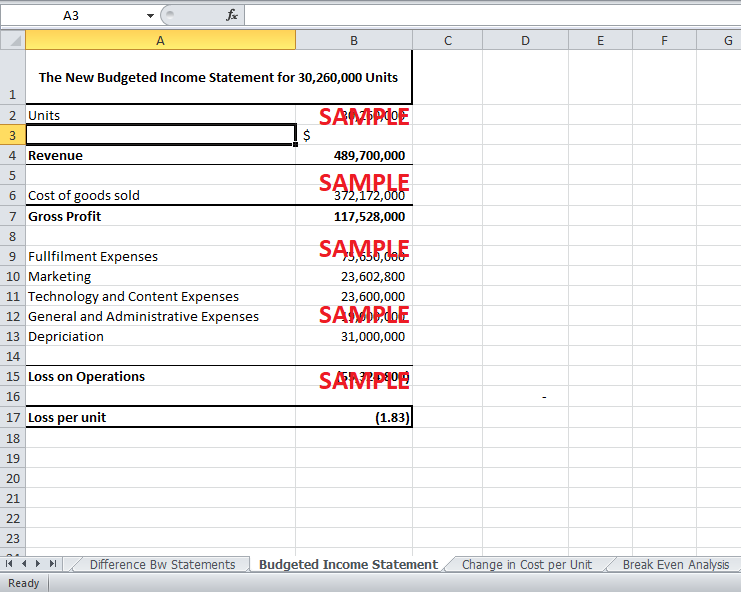
2. Prepare a flexible budget for EntertainmentNow.com for the past year, flexing solely on total actual units sold.
The budgeted income statement at the beginning of the year was prepared by using the budgeted sales volume of 29.76 million. The actual number of units sold at the end of the year was 30.26 million. Hence, a revised budget has to be prepared by basing the costs on the actual number of units sold. This flexible budget is required to analyze the actual difference in losses between the actual and the planned losses.
The revised budget is shown in Exhibit 3. It retains all the prior assumptions, and only the number is changed the actual number. The fixed costs do not change with the sales volume. Therefore, they are kept constant. Conversely, the variable cost increases as the volume increases. The new budgeted gross margin rises to $117,528,000. The loss reported after accounting for the actual number of sales is $55,324,800.
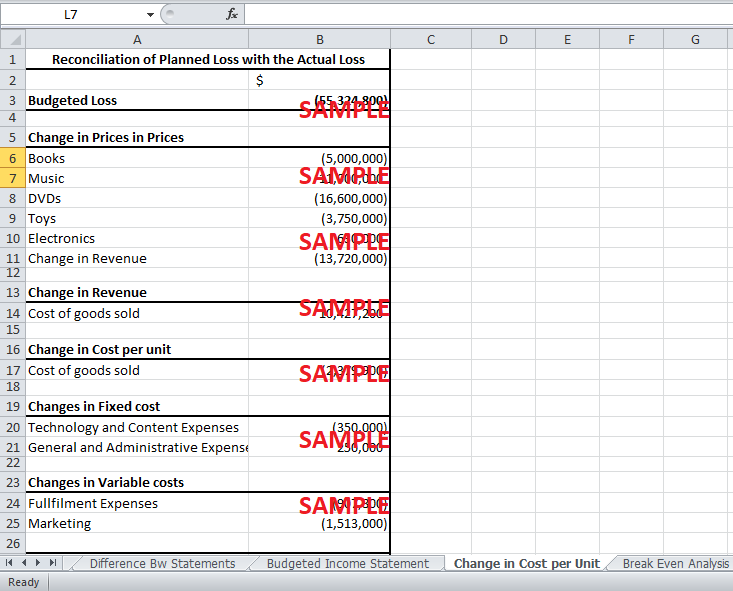
3. Quantify the impact on the net loss per item sold of each factor you noted in Question 1.
In order to quantify the impact of each factor noted above on the net loss per unit, a reconciliation statement is prepared in Exhibit 4 to reconcile revised planned profit of $55,324,800 with the actual loss of $63,518,300. The first main impact on the loss is the change in prices of the products. This change in prices causes an aggregate fall in revenue of $13,720,000. The reduced revenue also reduces the cost of goods sold, which is 76% of revenue, by $10,427,200. Conversely, the cost of sales rises due to the increase in percentage of revenue by 0.5%. The percentage rise leads to an increase in total cost of sales by $2,379,900. Hence, net fall in cost of sales is $8,047,300. Furthermore, as mentioned earlier, there is a net increase in fixed cost of $100,000 which also increases the loss.
Finally, the increase in variable costs lead to an increase in losses. The fulfillment expense per unit was $0.03 higher than the budgeted. Hence, the overall cost increased by $907,800. Likewise, the increase in marketing cost per unit by $0.05 caused an overall rise in marketing expenses by $1,513,000.
All the above factors were responsible for the difference in planned and actual losses for sales 30.26 million units of $8,193,500.
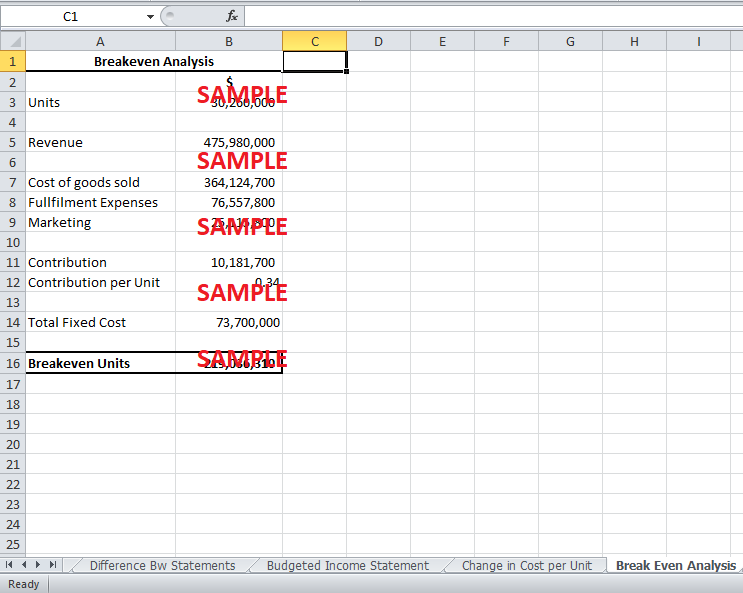
4. Assume that technology and content, general and administrative, and depreciation and amortization costs are fixed costs that total $73.7 million annually. Based on EntertainmentNow.com’s current sales revenue, cost of goods sold, fulfillment expenses, and marketing, what is the company’s break-even sales in units? Is this level of sales realistic? Why or why not?
Assuming that the fixed cost is $73.7 million, and all other variable costs and revenue are at the current level for 30.26 million units, the breakeven analysis is done as in Exhibit 5. The contribution for the current revenue and variable costs is $10,181,700. Thus, the contribution per unit is $0.34 per unit sold. The breakeven number of units is 219,036,310.
EntertainmentNow.com has a current level of sales of 30,260,000. Compared to the current level, the breakeven level of sales seems totally unreasonable. The high breakeven level of sales is the result of high fixed cost. The capital expenditure on technology must be treated as an asset in the balance sheet rather than charging it to the income statement. This should be done because the capital expenditure is not recurring and is a material amount. The wrong treatment of the expenditure has caused a significant increase in net loss. Similarly, the fixed cost of depreciation is too high for the firm which is only online. The fixed cost of general and administrative expenses is also very high.
In order to earn a profit, the business would have to increase sales. An increase in sales would increase revenue and contribution. Also, with the increase in sales, the loss per unit will also fall as the fixed costs are spread over more and more units.
The firm also needs to reduce its variable cost. A lower variable cost would increase contribution per unit which would reduce the breakeven number of units. An improvement in the efficiency of operations could also reduce the fixed cost. A reduction in fixed costs will also bring down the breakeven number of units.
Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Get Instant Access to This Case Solution for Only $19
Standard Price
$25
Save $6 on your purchase
-$6
Amount to Pay
$19
Different Requirements? Order a Custom Solution
Calculate the Price
Related Case Solutions
Get More Out of This
Our essay writing services are the best in the world. If you are in search of a professional essay writer, place your order on our website.