Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
OSG Corporation: Hedging Transaction Exposure Case Solution
OSG is a multinational corporation specializing in manufacturing and selling of cutting tools and parts used by industries worldwide. The company established in 1938, is based in Japan but has strong overseas sales in a number of countries across the Americas, Europe and Asia. Due to huge overseas sales, OSG faces increasing foreign exchange transaction exposure on its outstanding imports and exports denominated in foreign currency. Thus, the company vows to explore the various financial techniques available to it in order to mitigate the foreign exchange transaction risk. The company has to choose between whether to go with no hedging, selective hedging or mandatory hedging and within hedging, whether and how to use the hedging techniques of forward contracts, money market hedging and options.
Following questions are answered in this case study solution:
-
Explain non-hedging techniques for OSG to minimize transaction exposure, if any.
-
What are the costs of alternatives for reducing short term foreign currency risk? Assume OSG has an account receivable of US$1 million. Use the information provided in Appendix 1 for this account payable case of US$1 million to a US company. Which of the possible hedging methods presented in the case should OSG use if they expect the dollar to depreciate versus the yen during the next three months? Use the information provided in Exhibit 10.
-
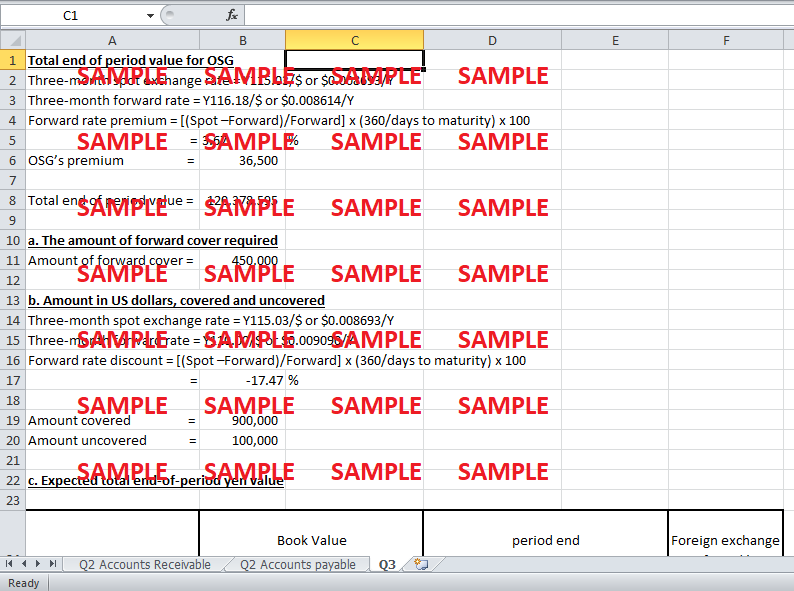
Suppose that OSG undertakes the same mandatory hedging policy as S. Corporation, the American company whose minimum forward-cover schedule is shown in Exhibit 9. Apply this schedule to the US$1 million account receivable case for OSG and find the expected total end-of-period value of the position taken by OSG. OSG expected to receive a US dollar (foreign currency) payment of US$1 million in three months. The spot rate was Y115.03/$, and the forward rate Y116.18/$ as shown in Appendix 1. Use Exhibit 10 for minimum forward-cover. Note that the yen is the home currency for OSG.
a. What would be the amount of forward cover required?
b. If the spot rate in three months was expected to be Y110.00/$, what would be the amount in US dollars, covered and uncovered?
c. What would be the expected total end-of-period yen value of the position taken in part (b)? Suppose the spot rate in three months will be Y115.00/$.
OSG Corporation Hedging Transaction Exposure Case Analysis
1. Explain non-hedging techniques for OSG to minimize transaction exposure, if any.
There are two non-hedging techniques available to OSG to minimize transaction exposure.
Invoicing in Yen
Under this policy, OSG can invoice its buyer in yen instead of the buyer’s home currency. Thus, no matter what happens to the foreign exchange rate, OSG will get its payment in yens and transaction exposure will be nullified; the transaction risk has been virtually shifted from OSG to the buyer. However, this approach has some challenges. Unless you are a US exporter, with your home currency, the US dollar, being the key international trade currency, demanding foreign buyers to pay in your home currency renders you less competitive in the market.
Netting Out
The second method to minimize foreign exchange transaction risk for OSG is by netting the risks out through frequent and diverse transactions. OSG is a large multinational corporation, and there are two reasons as to why its transaction exposure can be effectively mitigated by netting out:
-
OSG does frequent and large amount of foreign currency transactions with its subsidiaries as is reflected in its sales figures. Thus, the ups and downs of exchange rates are normalized over the big number of transactions.
-
OSG does transactions in many different currencies as it has a business in many different countries across Americas, Europe and Asia. Hence, an unexpected appreciation in one currency against the yen can be netted off by depreciation in some other currency.
Hence, although OSG’s overall risk cannot be completely nullified but can be mitigated to extent by netting off.
2. What are the costs of alternatives for reducing short term foreign currency risk? Assume OSG has an account receivable of US$1 million. Use the information provided in Appendix 1 for this account payable case of US$1 million to a US company. Which of the possible hedging methods presented in the case should OSG use if they expect the dollar to depreciate versus the yen during the next three months? Use the information provided in Exhibit 10.
Alternatives for Reducing Short-term Currency Risk on Accounts Receivable
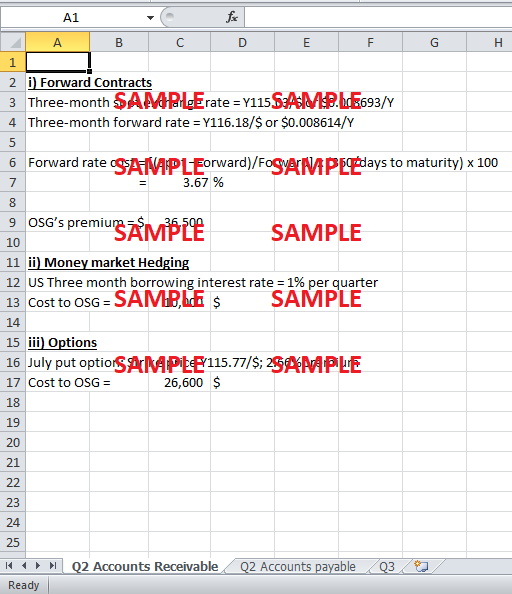
i. Forward Contracts
OSG can enter into a forward contract of selling US $ 1 million in 90 days at the three-month forward rate of Y116.18/$. At the end of 90 days, OSG will be able to convert the received US $ 1 million into yen at this fixed stated rate.
Cost of Forward Contract
Three-month spot exchange rate = Y115.03/$ or $0.008693/Y
Three-month forward rate = Y116.18/$ or $0.008614/Y
Since the dollar is expected to appreciate against the yen, there is going to be a forward premium, and OSG will gain relative to the current spot rate instead of incurring any cost with the forward contract.
Forward rate cost = [(Spot – Forward) / Forward] x (360 / days to maturity) x 100
= [(0.008693 - 0.008614) / 0.008614] x (360 / 90) x 100
= 3.65%
OSG’s premium = $ 1 million x 0.0365
= $ 36,500
ii. Money Market Hedging
OSG could also use money market hedging techniques. Under this method, OSG will take a loan of US $ 1 million and convert it into Yen. At the time of completion of 90 days, OSG will return the principle amount of US $ 1 million, plus the accrued interest using the US $ 1million receivable realized.
Cost of Loans
US three month borrowing interest rate = 1% per quarter
Cost to OSG = 1% x 1 million
= 10,000 $
iii. Options
OSG can also hedge the risk by buying a 3-month put option. This option will give OSG a right to sell US $ 1 million at the exercise price on or before the 3 months completion date.
Cost of Options
OSG will incur the cost of exercising the option equal to the stated premium of the option.
July put option: Strike price Y115.77/$; 2.66% premium
Cost to OSG = 2.66% x 1 million
= 26,600 $
iv. Accounts Payable Case of US $ 1 Million
The three methods can be evaluated one by one:
Forward Contract
The spot exchange rate is Y115.03/$, and the dollar is expected to depreciate during the next three months. This means that the future spot rate is expected to be below Y115.03/$ at least. However, the three month forward rate is Y116.18/$, which means the holder of this contract will buy US dollars for more yens then they would have if they had bought them at the spot exchange rate on that day. Hence, buying the future contract is not useful.
Money Market Hedging
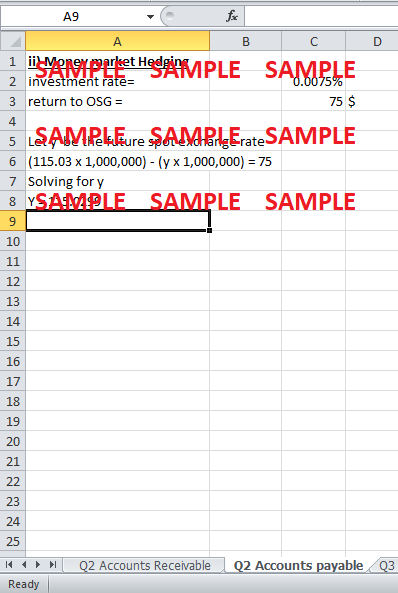
OSG can convert yens to US $ 1 million at the current spot exchange rate and invest them in the bank today. The amount can be withdrawn after three months and used to clear the accounts payable payment. OSG will also earn 0.0075% interest on its investment.
However, since the dollar is expected to depreciate, OSG might be better off by not taking the above approach and simply converting yens to US $ 1 million on the spot exchange rate on the three months end-date and make the payment.
Whether to convert on today’s spot rate and invest, or convert on the future spot rate, really depends on the comparison between the investment interest rate and the extent of depreciation of the dollar.
The investment rate is given to be 0.0075%. The return to OSG will be 0.000075 x 1 million = 75 $ only.
We can calculate the future spot exchange rate on or below which OSG can earn more than 75$ and should take the future spot exchange rate option instead of current spot rate and investing option.
Let y be the future spot exchange rate
(115.03 x 1,000,000) - (y x 1,000,000) = 75
Solving for y
Y = 115.0299
Hence, even if the dollar falls only from Y115.03/$ to Y115.0299/$, OSG is better off by converting on the future spot exchange rate. The money market hedging option doesn’t seem very good given dollar is expected to depreciate.
Options
OSG can buy a 3 month call option for US $ 1 million, strike price Y115.73/$; 1.29% premium to cover itself if the dollar was expected to appreciate, but since the dollar is expected to fall, OSG will never exercise this option. Hence, using options to hedge in this case is out of the question.
3. Suppose that OSG undertakes the same mandatory hedging policy as S. Corporation, the American company whose minimum forward-cover schedule is shown in Exhibit 9. Apply this schedule to the US$1 million account receivable case for OSG and find the expected total end-of-period value of the position taken by OSG. OSG expected to receive a US dollar (foreign currency) payment of US$1 million in three months. The spot rate was Y115.03/$, and the forward rate Y116.18/$ as shown in Appendix 1. Use Exhibit 10 for minimum forward-cover. Note that the yen is the home currency for OSG.
Total End of Period Value for OSG
Three-month spot exchange rate = Y115.03/$ or $0.008693/Y
Three-month forward rate = Y116.18/$ or $0.008614/Y
Forward rate premium = [(Spot – Forward) / Forward] x (360 / days to maturity) x 100
= [(0.008693 - 0.008614) / 0.008614] x (360 / 90) x 100
= 3.65%
OSG’s premium = $ 1 million x 0.0365
= $ 36,500
Total end of period value = (1,000,000 x 116.18) + (36,500 x 115.03)
= Y 120,278,595
Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Get Instant Access to This Case Solution for Only $19
Standard Price
$25
Save $6 on your purchase
-$6
Amount to Pay
$19
Different Requirements? Order a Custom Solution
Calculate the Price
Related Case Solutions
Get More Out of This
Our essay writing services are the best in the world. If you are in search of a professional essay writer, place your order on our website.