Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
American Barrick Resources Corporation Managing Gold Price Risk Case Solution
American Barrick is a gold mining company that has a very effective price risk management program in place. The company hedges its gold price risk in order to gain greater financial stability, as well as operational and financial predictability. This allows them to plan their way forward with greater effectiveness. The first task is to determine the level volatility experienced by the company’s stocks with respect to changes in the price of gold. For this, data regarding both the financial and operational aspects of the company is to be used to make future projections of cash flows, which are to be discounted to reach the company’s intrinsic value. Then a sensitivity analysis needs to be conducted to determine the change in this intrinsic value with respect to change in gold prices. Once the volatility has been determined, hedging against its risk needs to be discussed using the information given in the case.
Following questions are answered in this case study solution:
-
In the absence of a hedging program using financial instruments, how sensitive would Barrick stock be to gold price changes? For every 1% change in gold prices, how might its stock be affected? How could the firm manage its gold price exposure without the use of financial contracts?
-
What is the stated intent of ABX’s hedging program? What should be the goal of a gold mine’s price risk management program?
-
What would convince you that a price risk management program created value for its shareholders ex ante?
-
How would you characterize the evolution of Barrick’s price risk management activities? Are they consistent with the stated policy goals?
-
How should a gold mine which wants to moderate its gold price risk compare strategies (using futures, forwards, gold loans, or spot deferred contracts) with insurance strategies (using options)? On what basis should these decisions be made? Once a firm has decided on either a hedging or an insurance strategy, how should it choose from among specific alternatives?
-
What is a “spot deferred contract?” Is it an option? a forward contract? Why has ABX chosen to rely on spot deferred contracts relative to other gold derivatives?
American Barrick Resources Corporation Managing Gold Price Risk Case Analysis
1. In the absence of a hedging program using financial instruments, how sensitive would Barrick stock be to gold price changes? For every 1% change in gold prices, how might its stock be affected? How could the firm manage its gold price exposure without the use of financial contracts?
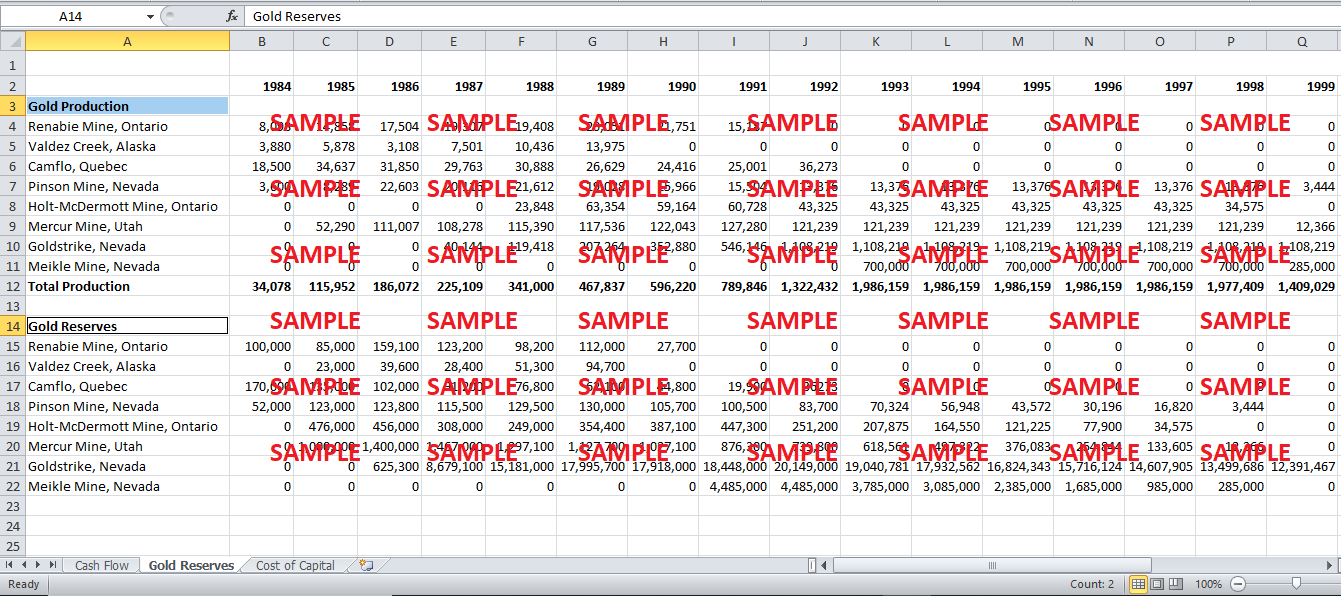
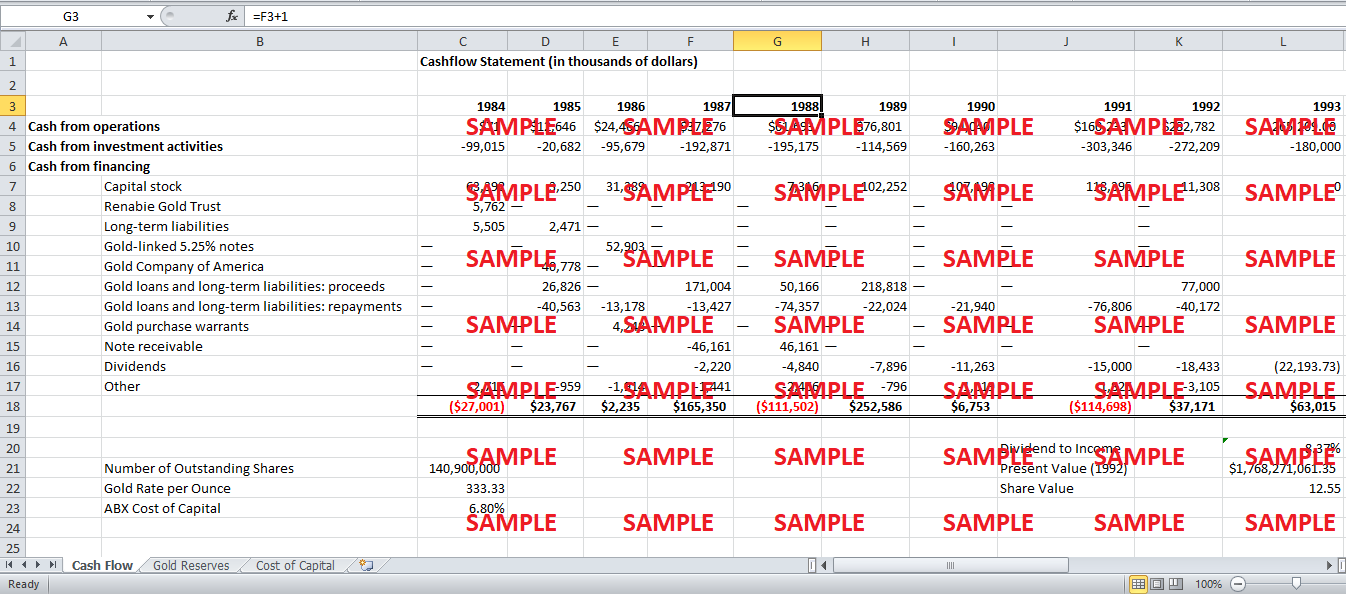
Any firm’s stock reflects that firm’s intrinsic value, and intrinsic value is determined by the projected cash flows of the firm. American Barrick’s intrinsic values can also be calculated using the firm’s projected cash flows. In order to do that, the analysis would not only require American Barrick’s projected operational inflows and outflows, as well as those from investing and financing. In order to simplify, the firm can be assumed to be in its mature stage, meaning it will be making investments and raising finances at roughly the same rate as in the recent years, except for those relating to the Meikle Mine in Nevada. This also means that all future operational inflow will be dependent on current gold production, which currently stands at 1,322,432 ounces of gold per year, and reserves, which stand at 25,708,700 ounces of gold. Since, by 1995, gold production is expected to be close to 2 million ounces, it will determine the production of the new mine. Using this, and the latest gold rates, the total operational inflow can be calculated. Similarly, operational outflow can also be calculated using the cost of production values given in the case.
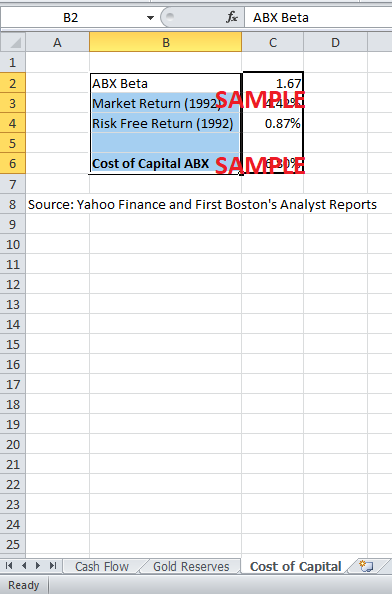
The second aspect of any valuation model is the outstanding stock and discount rate used to value the stock. Since American Barrick is being assumed to be in the mature stage, it is safe to assume that the firm’s cost of capital will remain the same. The cost of capital can be found by using American Barrick’s 5-year investment beta and the capital asset pricing model. The outstanding stock of American Barrick is 140.9 million shares.
Using all this information cash flow projections can be made for the firm and it’s stock's intrinsic value, which comes out to be $12.55 at the current gold price. With the financial model of the firm in hand, it is possible to test the sensitivity of the firm’s intrinsic value with respect to changes in the price of gold if the firm adopts a policy of not hedging its position in the market. The table in exhibit-A elaborates the results of the sensitivity analysis. It can be seen that a 1% change in the gold price can cause a 2.57% change in the firm’s stock value. This shows that the firm’s stock price is extremely sensitivity to change in the price of gold, therefore, the need to hedge against gold price fluctuations.
Using financial instruments is one way to hedge the risk of gold price fluctuations; however, if the firm does not wish to adopt this strategy then it can use operational measures to hedge some of the risk. Once again, just like in financial instruments, it requires some speculation as to what is the expected movement of gold price. The company can continue, or discontinue, production at different mines depending on the costs of production in order to control the supply and cost of production. For this, the firm will have to speculate the price of gold and make production plans accordingly. However, this process is not instantaneous, like financial contracts, and there is a limit to how much risk can be mitigated.
2. What is the stated intent of ABX’s hedging program? What should be the goal of a gold mine’s price risk management program?
According to the Board of Directors, the intention of American Barrick’s hedging program is to attain financial stability, by protecting the firm against dips in gold prices. It does so in order to better predict the firm’s operational and financial needs, and plan its cash flows, which allow the firm to provide its investors with more steady returns to their investment.
As can be seen in Exhibit-A, the stock value of a gold mining firm is directly related to the price at which it is able to sell its production, and extremely sensitive to it. Therefore, in order to attain financial stability the company needs to stabilize the price at which it can sell its production. This is because it allows management to predict the direction the company is going in, in terms of both operations and finances, with greater accuracy. It also allows investors to mitigate the risk of return in their investment. Therefore, it is the goal of a firm’s price risk management program to speculate price changes in the gold market and to adjust its position so as to protect itself from downside risk while enabling the company to benefit from the upside as much as possible.
3. What would convince you that a price risk management program created value for its shareholders ex ante?
As discussed before, value to shareholders is created by increased cash flows to the company. Therefore, for a risk management program to create value to the shareholders it has to result in an influx of cash, or income, greater than it would have been without it. For example, if the price risk management program of the company speculates a drop in gold prices, and secures Forward Contracts, then when the price decreases the company will be able to sell its production at a higher than market rate. Such a move would have created value for the shareholders as it did in the case of American Barrick during the first Gulf War.
4. How would you characterize the evolution of Barrick’s price risk management activities? Are they consistent with the stated policy goals?
As mentioned, the stated goals of American Barrick’s price risk management policy are to reduce the volatility experienced by the firm and to ensure increased value to shareholders. In the beginning, since hedging was an uncharted territory for the American Barrick management, it was very cautious with its approach and only limited its scope to very simple instruments like gold-linked loans and other gold financing. However, as time went on, the company started to increase the level of participation in hedging instruments, and began to experiment with newer and more complicated instruments like options contracts and combinations of options to create different hedging positions. The company in order to benefit even more from the upside potential also started dealing in forward contracts and spot deferred contracts.
Even though the company lacked the in-house training, know-how, and financial models to price the contracts it participated in, it was very successful in executing them by using market comparatives. Presently the company deals in all forms of hedging instruments, and has had significant accomplishments as is obvious from Exhibit-B.
Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Get Instant Access to This Case Solution for Only $19
Standard Price
$25
Save $6 on your purchase
-$6
Amount to Pay
$19
Different Requirements? Order a Custom Solution
Calculate the Price
Related Case Solutions
Get More Out of This
Our essay writing services are the best in the world. If you are in search of a professional essay writer, place your order on our website.