Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Beta Management Company Case Solution
Wolfe manages a small investment portfolio that takes varying levels of exposure in a single stock index - the Vanguard 500 Index - that mimic the return on S&P500 index. During the recent economic downturn, Wolfe has performed well by lowering his exposure to equity markets and investing the excess funds into money market instruments. The improved performance has allowed Wolfe to attract new investments, but it has also attracted criticism that Wolfe does not engage in active stock selection. Thereby, Wolfe is contemplating investing in two small-cap stocks. However, he is concerned that the variability of these stocks is very high and it might increase the riskiness of the overall portfolio. We show that although the individual variability of the stocks is high, the overall risk of the portfolio will remain low because the stocks are perfectly correlated with the existing investment - Vanguard 500 Index. Moreover, we calculate the beta for each stock relative to the Index and estimate the expected return on each stock using the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM).
Following questions are answered in this case study solution:
-
What is Wolfe’s current investment strategy? What kind of adjustment is she considering?
-
Calculate the variability (standard deviation) of the stock returns of California REIT (CREIT) and Brown Group (BG) during the past two years. How variable are they compared with Vanguard Index 500 Trust? Which stock appears to be riskiest?
-
Suppose Beta’s position had been 99% of equity funds invested in the index fund, and 1% in the individual stock. Calculate the variability of this portfolio using each stock. How does each stock affect the variability of the equity investment, and which stock is riskiest? Explain how this makes sense in view of your answer to Question 2 above.
-
Perform a regression of each stock’s monthly returns on the Index returns to compute the “beta” for each stock. This regression is called the Market Model in the literature. How does this relate to the situation described in Question 3 above?
-
How might the expected return for each stock relate to its riskiness?
-
What do you think about the move to a more active stock-picking strategy?
-
Try to derive the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) equation for the two stocks. Try to work out this question by assuming that Beta’s position had been 99% of equity funds invested in the index fund, and 1% in a riskless money market account. Imagine that you can switch from the money market account to CREIT, BG, or the index fund. Think about the condition for Sarah to be indifferent between switching to CREIT (or BG) and switching to the index.
Beta Management Company Case Analysis
1. What is Wolfe's current investment strategy? What kind of adjustment is she considering?
In the initial period, Wolfe started investing his client's funds in a selected few indexed funds. This strategy made sense because Wolfe did not have sufficient clients and resources to actively select specific stocks for its clients. Wolfe further streamlined this approach by limiting its investment to a single indexed fund - the Vanguard 500 Index. The Vanguard 500 was a suitable index because its returns closely matched the returns on the S&P500 stock index. The S&P500 is an index of the five hundred largest stocks in the United States, and it is believed to be well diversified. However, Wolfe did not follow a passive investment strategy because it studied the market movements and altered its stock exposure accordingly. For instance, if Wolfe expected a market downturn, it would limit its investment in the Vanguard 500 index and invest a larger proportion in money market funds that provide a fixed return. This strategy worked very well during the recent market downturn and attracted many new clients for Wolfe. However, Wolfe was also criticized for not undertaking an active selection of stock for its clients. In response to the criticism, Wolfe was now contemplating adding a few individual stocks to its portfolio and hired some analysts to assist with the research. Wolfe considered that small-cap stocks would be a good addition because the portfolio's current investment already provided adequate exposure to large S&P500 stocks. However, the excessive variability in the individual stock worried Wolfe, as they may increase the risk of the overall portfolio.
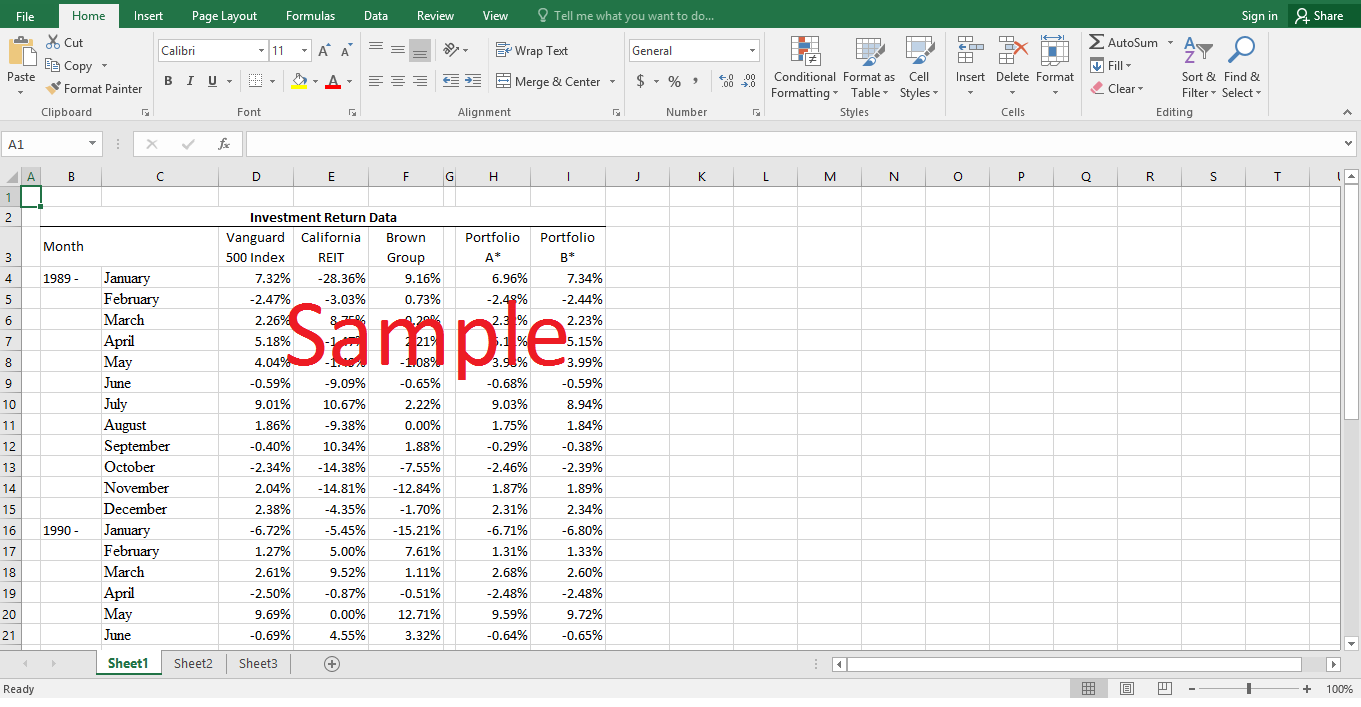
2. Calculate the variability (standard deviation) of the stock returns of California REIT (CREIT) and Brown Group (BG) during the past two years. How variable are they compared with Vanguard Index 500 Trust? Which stock appears to be riskiest?
The standard deviation can be obtained by taking the square root of the variance of the returns. The variance in any stock's returns is obtained by taking an average of the squared difference between average (mean) return and each individual return over a specified time period. It is much easier to calculate the standard deviation in automated software such as Microsoft Excel. Therefore, the monthly returns data provided for the Vanguard 500 Index, California REIT, and Brown Group in the appendix of the case study have been transferred to the attached spreadsheet. The mean (average) return and standard deviation of the return have also been calculated for each of the three sets of potential investments. The standard deviation in returns for California REIT and Brown Group are approximate twice the standard deviation in returns on Vanguard Index. Vanguard Index has a standard deviation of 4.61%. On the other hand, California REIT and Brown Group have standard deviations of 9.24% and 8.17% respectively. Similarly, the Vanguard Index also has a higher average (mean) return than the other two stocks than the two individual stocks. The mean returns on the individual stocks are negative during the observed time period, but that could be a consequence of the prevailing recession. It appears that the California REIT is the least attractive stock because it has the lowest mean return of negative 2.27% and the highest standard deviation of 9.24%.
3. Suppose Beta's position had been 99% of equity funds invested in the index fund, and 1% in the individual stock. Calculate the variability of this portfolio using each stock. How does each stock affect the variability of the equity investment, and which stock is riskiest? Explain how this makes sense in view of your answer to Question 2 above.
There can be two possible portfolios under the provided circumstances. Portfolio A is an imaginary portfolio comprising 99% of investment in Vanguard 500 Index and the remaining 1% of the investment in California REIT. Similarly, Portfolio B is a hypothetical portfolio consisting of 99% funds invested in Vanguard 500 Index and the remaining 1% funds invested in Brown Group. The attached excel sheet details the monthly return that could be obtained from both the portfolios. The monthly returns are simply the weighted average of the returns on individual investments from which the portfolio is constructed. Once we have the monthly returns on each of the hypothetical portfolios, the standard deviation or variability of the portfolios can be easily calculated in the excel spreadsheet. It is revealed that the variability of Portfolio A - composed of Vanguard 500 Index and California REIT - is 4.57%, while the variability of Portfolio B - composed of Vanguard 500 Index and Brown Group - is 4.61%. It is interesting to note that the overall variability of the portfolio is much lower than the variability of the individual stocks. In fact, the variability of Portfolio A is lower than the individual variations in both Vanguard 500 Index returns and California REIT returns. This result is plausible if it is found that the correlation between Vanguard 500 Index and California REIT is less than one. A correlation coefficient of less than one will ensure that variations in Vanguard 500 Index and California REIT returns offset each other such that the portfolio variation is lowered.
4. Perform a regression of each stock's monthly returns on the Index returns to compute the "beta" for each stock. This regression is called the Market Model in the literature. How does this relate to the situation described in Question 3 above?
The regression line is a best-fit linear line between the returns of Vanguard 500 Index - plotted on y-axis - and the returns of each stock - plotted on x-axis. The gradient or slope of the resulting best-fit line is the beta for each stock. There are two ways to calculate the beta. One way is to use the slope function in Microsoft Excel to calculate the beta. An alternative way is to calculate the beta directly from the provided data. The beta is defined as the covariance between the individual stock's return and the return of the market, divided by the variance of the market. Note that the Vanguard 500 Index serves as a substitute for the market in this case, while the individual stocks are California REIT and Brown Group. Using this methodology, the betas for both of the individual stocks are calculated in the attached spreadsheet. The beta for California REIT is 0.14, while the beta for Brown Group is 1.11. Note that these betas are also the slopes coefficients in the regression equations. The betas provide an adequate explanation for the results obtained in the previous question. Brown Group is an aggressive stock with a beta higher than one, while California REIT is a defensive stock with beta close to 0.14. The implication is that the return on California REIT is expected to vary less with changes in Vanguard 500 Index (market) returns. Therefore, the combined variability of California REIT and Vanguard 500, as measured by the variability in Portfolio A in the previous question, is lower than the combined variability of Brown Group and Vanguard 500 Index, as measured by Portfolio B
Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Get Instant Access to This Case Solution for Only $19
Standard Price
$25
Save $6 on your purchase
-$6
Amount to Pay
$19
Different Requirements? Order a Custom Solution
Calculate the Price
Related Case Solutions
Get More Out of This
Our essay writing services are the best in the world. If you are in search of a professional essay writer, place your order on our website.