Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Jimmy Fu and Moog, Inc. Understanding Shareholder's Equity (Brief Case) Case Solution
In the first transaction, the stock split will have no effect on the total shareholder equity, but it will increase the number of shares outstanding by 50%. The increase in the outstanding shares is shown in the spreadsheet calculations. If Jimmy was holding any stock before the split, his share holding would also increase in accordance with the split. However, the value of his holdings would remain the same as the market price of the stock would adjust in conformity with the stock split. The options would also adjust after the split, and their value would remain the same.
The second transaction would reduce the number of Class A shares outstanding by 112,119. The balance of the treasury stock would also increase by the amount paid for the shares. Since the treasury account is a contra-equity account, the amount paid for the share purchase would result in a reduction in total shareholders’ equity. The shares were bought from the open market at the traded price. Therefore, the repurchase is not likely to affect the market price of the remaining shares and the value of Jimmy’s stock and options would remain unaffected.
Following questions are answered in this case study solution:
-
Put yourself in Jimmy’s shoes and using information contained in exhibit 1. Explain the changes in the equity section of the balance sheet that occurred as a result of the five transactions which jimmy found referenced in Moog’s 2007 10-K filing. Discuss how they might affect the value of Jimmy’s restricted stock and options (in terms of the direction as opposed to magnitude of value changes) had he been working for the firm at the time. Where appropriate, provide details on any changes to the number of shares authorized, issues and outstanding as well as the appropriate valuation for balance sheet purposes.
-
Prepare the Shareholders Equity section of the Balance Sheet for Moog Inc. as at September 29, 2007.
-
Given your answer to the previous question and the additional information regarding transactions in 2008 detailed above, prepare and describe in detail the set of equity related transactions which would generate the Shareholder’s Equity section of the Balance Sheet for Moog Inc. as at September 28, 2008. Be specific in your responses and show all the effects of each transactions which result in a perfect replication of the 2008 Balance Sheet, you should document the effects of those transactions which you think occurred and provide the equity section of a pro-forma Balance Sheet for September)
-
For fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2005, the FASB requires that an expense (equal to the fair value of the option being granted) must be charged upon issuance of employee stock options. Assuming that Jimmy was issued a grant of 12,000 options which he will exercise once they are all vested when the stock price has risen to $10 per share, describe in detail how to account for the options in each fiscal year from the grant date until the exercise date. You should assume that the fair value of each option was $3 on the grant date when the stock price was $5.00 and that the first options would vest on the grant date. You should assume that the company issues new shares to satisfy its obligation.
Jimmy Fu and Moog Inc Understanding Shareholder s Equity Brief Case Case Analysis
1. In the third transaction, the previous purchase of the share by the company must have been recorded in the treasury shares account. Since the company is now issuing these shares to the employees, the balance of the treasury shares must be reduced by the initial amount in which it was increased when the stock was purchased. The transaction will increase total shareholder’s equity. However, the number of shares would increase traded in the market would increase and the price paid (exercise price) for additional shares is likely to be lower than the market price, which would lead to a reduction in market price and a decline in value of Jimmy’s stock and options.
The fourth transaction would have no effect on the total shares outstanding of all the classes. However, it would reduce the number of Class B shares and incur a corresponding increase in Class B shares. However, the total shareholders’ equity will remain the same. The price of Class A and Class B shares may be affected by the transaction. For example, if Class A shares are trading at a higher price than Class B shares, the conversion of the lower-value Class B shares into the higher-value Class A shares might result in a slight decrease in the value of Class A shares and a slight increase in the value of Class B shares. Therefore, the change in the value of Jimmy’s shares would depend on the class of shares that he is holding.
In the last transaction during 2007, the $16.5 million loss of foreign exchange transactions may be recorded in other comprehensive income, while the profit of $64.79 million would increase the retained earnings by the same amount, as there are no dividend payments. The net effect would be an increase in total shareholders’ equity of $48.29 million. The impact of this transaction on stock price in uncertain. If the net income is bigger than expectations, the stock price might increase and Jimmy might benefit. In the other case, stock price might remain the same or decrease if the net income is equal to or lower than expectation, respectively.
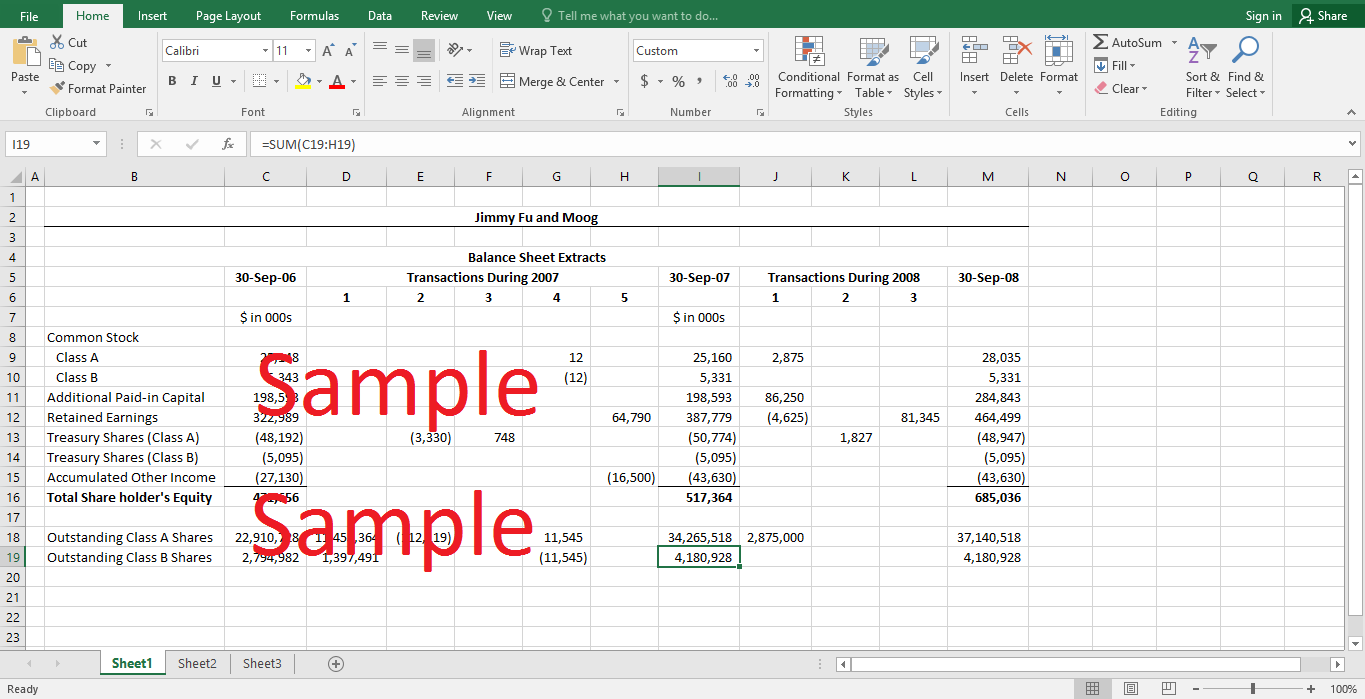
2. The shareholders equity section of the balance sheet for the year ended September 30, 2007 is shown in the attached excel spreadsheet. The effect of each of the transactions, during the year, on different equity accounts is also shown.
3. For the year 2008, the first transaction would increase the amount of outstanding shares by 2,875,000. The Class A shares account would increase by the par value of the shares issued, which is $2.875 million. The difference between the par value and the actual gross proceeds from the share issue would be recorded in additional paid-in capital – this amount equals $86.25 million. The costs incurred for the share issue equals the difference between gross proceeds from the issue and the net proceeds. This difference of $4.625 million would be recorded as an expense in the income statement and reflected in the retained earnings account. The cash flow from this transaction would increase by the amount of $84.25 – the net proceeds from the issues. However, this amount would be used to repay outstanding credit facility borrowing.
For the second transaction, it is assumed that the average exercise price of the stock options would be the same as the average purchase price of $5.33. The balance of the treasury shares account will be reduced by the amount paid for the shares. As treasury shares account is a contra-equity account, the total shareholders’ equity would increase. The cash balance of the company would also increase by the total exercise price paid by the employees.
In the absence of any dividends, the reported net income in the third transaction would be result in an increase in retained earnings by the same amount.
Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Get Instant Access to This Case Solution for Only $19
Standard Price
$25
Save $6 on your purchase
-$6
Amount to Pay
$19
Different Requirements? Order a Custom Solution
Calculate the Price
Related Case Solutions
- John Deere Component Works (A) Case Solution
- Johnson Controls, Automotive Systems Group- The Georgetown, Kentucky Plant Case Solution
- Jollibee Foods Corp. (A) International Expansion Case Solution
- Jones Electrical Distribution Case Solution
- Journey to Sakhalin- Royal Dutch-Shell in Russia (A) Case Solution
Get More Out of This
Our essay writing services are the best in the world. If you are in search of a professional essay writer, place your order on our website.