Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Tonka Corporation Case Solution
1985 and 1986 were the most successful years in the history of Tonka Corporation, the fifth biggest toy maker in the United States. The $293 million in sales and $22 million in profit in 1986 were both record highs. Tonka replaced its long-term debt in January 1987 and sold over a million shares of common stock in December 1986, both of which reduced the company's equity and increased its liquidity. There are 800 toy makers in the United States, but only the biggest have found success in reducing sales and financial leverage via diversification. The toymaker can also adapt to changing weather conditions. Not every one of them has been positive, either. Around $70 million in sales in recent years may be attributed to Tonka Corporation's classic range of heavy metal toy trucks, bulldozers, backhoes, and construction equipment. However, in recent years the firm has expanded into other areas, such as dolls and other items that might enhance a girl's attractiveness.
Following questions are answered in this case study solution:
-
How much business risk does Tonka face?
-
How much potential value, if any, can Tonka create for its shareholders at each of the proposed levels of debt? How would leveraging up affect the company’s taxes?
-
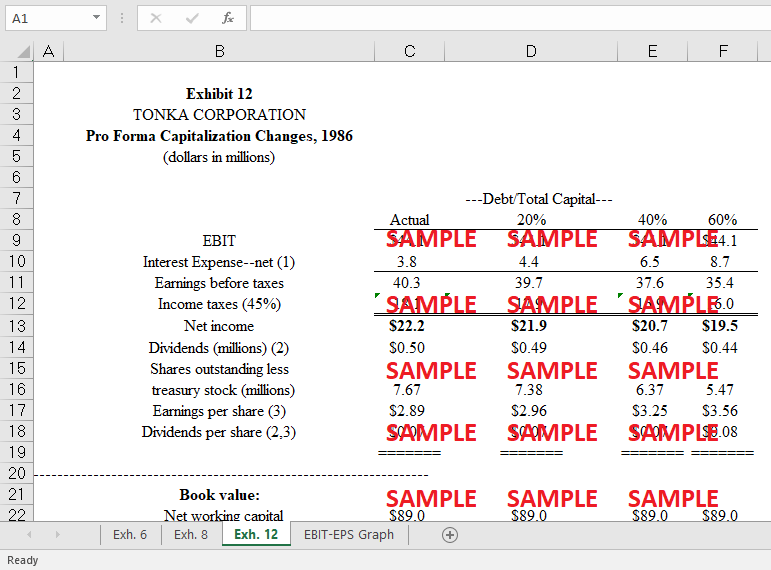
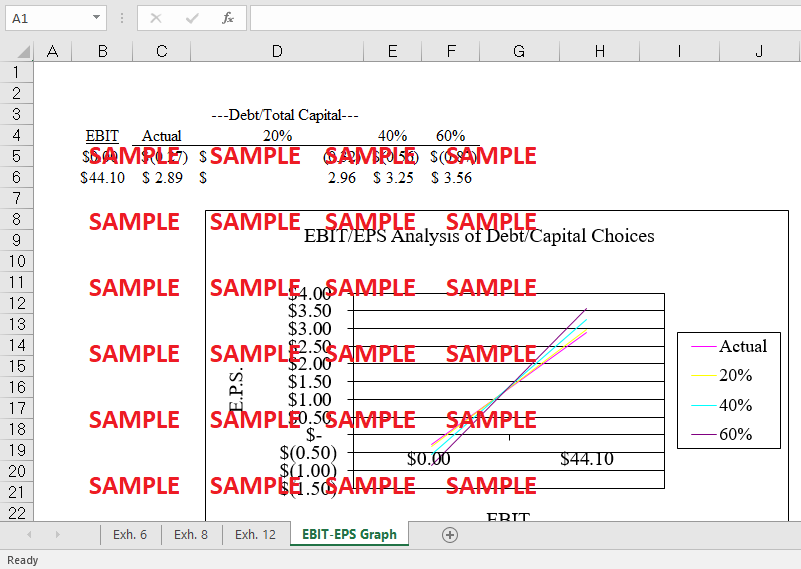
How much financial risk would Tonka face at each of the proposed levels of debt shown in case Exhibit 12? How would the capital markets react to a decision by the company to increase the use of debt in its capital structure?
-
What capital structure would you recommend as appropriate for Tonka?
-
How might Tonka implement an aggressive capital-structure policy? What are the alternative tactics for leveraging up?
-
What arguments would you advance to persuade Tonka’s management to adopt your recommendation?
Case Study Questions Answers
1. How much business risk does Tonka face?
Tonka, just like any other firm, is vulnerable to the dangers that come with engaging in activities such as penetrating new markets, seeing shifts in the value of its currency, and declaring bankruptcy. Tonka is in competition with industry titans such as Coleco, Hasbro, Kenner Parker, and Mattel, all of which bring in more yearly income than Tonka does on its own. It is quite likely that the availability of items manufactured by competing firms will function as a barrier to the increase of market share held by The Tonka as well as its profit margins. Because of the nature of Tonka's business, which requires it to operate on a worldwide scale, the firm is susceptible to swings in the rates at which currencies are exchanged when it comes to translating the native currency of its overseas operations into that of the United States. There is the danger of incurring significant losses if the value of other foreign currencies undergoes major swings in contrast to the value of the dollar. Because of the status of the global economy, businesses must contend with a variety of challenges. These concerns include shifts in interest rate environments as well as inflationary pressures, both of which can have a significant impact on the bottom line of a business. According to a review of the company's capital structure, the combination of revolving credit and term loans is Tonka's most significant source of finance. This is the principal source of financing for the firm. If a company decides to finance its operations using debt, there is a greater possibility that it might run into financial problems if it is unable to pay off the interest that has accrued on loan. This is because there is a greater likelihood that the company will run into problems if it is unable to pay off the interest.
2. How much potential value, if any, can Tonka create for its shareholders at each of the proposed levels of debt? How would leveraging up affect the company’s taxes?
The current market value of the company's shares is $ 20.27 million, based on historical data and present conditions. With 20% debt, the market value of each share is $ 20.62, and the value generated at this level of debt is $ 0.35 ($20.62 minus $20.27). At 40% debt, value is $ 21.94 -$ 20.27 = $ 1.67 per share, and at 60% debt, value is $ 23.27 -$ 20.27 = $ 3.00 per share. Increasing the company's leverage or debt will reduce its tax liability. This is because interest paid on debt is tax deductible, resulting in reduced after-tax earnings. As a result, if a corporation takes on more debt, it will pay fewer taxes. Numerous indicators of economic health in the United States have improved since 1983. These include real gross domestic product growth, personal disposable income, etc. The decline in the unemployment rate, the consumer price index, and the prime lending rate have fueled these expansion rates. In fact, this is just the fourth year in a row of economic expansion for the United States. However, despite the decline in real GDP growth, there was a decrease in both unemployment and interest rates and a 2% rise in real per capita disposable income in 1986. Tonka had a 1.2% increase in revenue for the company in 1982, 1.4% growth in 1983, 1.8% growth in 1984, 2.9% growth in 1985, and 3.5% growth in 1986.
Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Get Instant Access to This Case Solution for Only $19
Standard Price
$25
Save $6 on your purchase
-$6
Amount to Pay
$19
Different Requirements? Order a Custom Solution
Calculate the Price
Related Case Solutions
Get More Out of This
Our essay writing services are the best in the world. If you are in search of a professional essay writer, place your order on our website.