Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Anagene Inc Case Solution
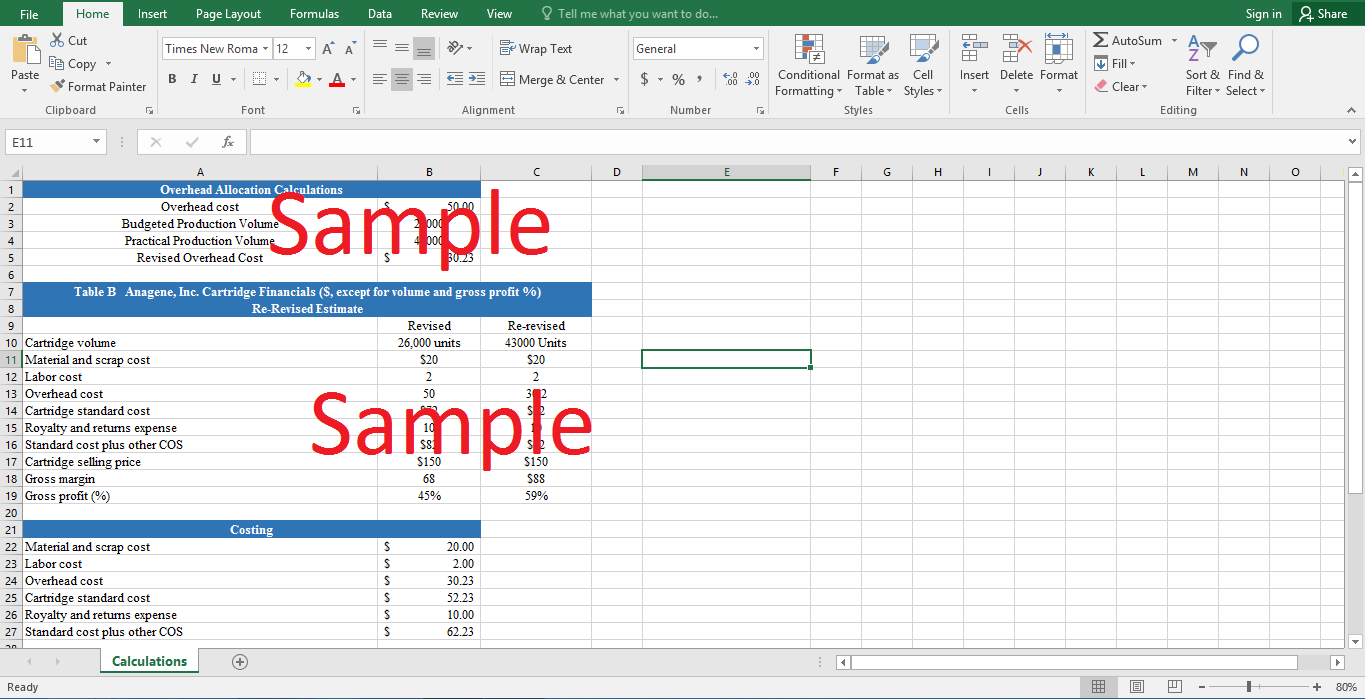
Anagene Inc. is faced with the dilemma of uncertain and unpredictable margins. The industry in which Anagene operates is relatively young and full of competition. However, the micro-arrays of Anagene are distinctive in their nature; therefore, Anagene enjoys rising trend in sales. The current costing system of Anagene takes budgeted volume as the base for measuring overhead costs. This method causes the margins to vary and profitability to decrease. Apart from this reason, the market dynamics of Genomic instrument industry pose unpredictability in spotting new customers. Moreover, the reuse of the cartridges from the customers also yields uncertain margins amounts. Kelly should seriously consider the overhead costs in the costing strategy as it allows the company to take into account the idle capacity. Fixed costs are an integral part of Anagene costing strategy and they should not be ignored by employing the variable contribution margins. The actual production yield insights on the variance analysis and the use of both the practical and budgeted level of production can be justified in any business. The practical capacity yields the overhead cost of $30. The final cost of cartridges comes out to be $62. As a result of employing this method, the gross margin increases by 14%.
Following questions are answered in this case study solution:
-
Describe Anagene’s competitive environment, including its industry, its specific customer base, its product / customer heterogeneity, and the major concerns facing Anagene.
-
Considering your answer to item 1, is it likely that the existing cost system may adversely and significantly affect decisions to emphasize certain products or affect profit? Why (a general answer is expected)?
-
What has caused the fluctuating margins for Anagene’s cartridges?
-
Should Kelly even be concerned with the assignment of overhead costs to cartridges and gross margins that include allocated overhead? Why not use variable contribution margin (selling price less variable costs, primarily materials) for management decision-making and reporting?
-
Refer to items 3 and items 4, what role does practical capacity, expected production, and actual production play in formulating an approach for assigning overhead? How are these matters useful to managers? Draw on text and readings for your answer.
-
What approach do you recommend that Daniel Yeltin adopt? Explain. For your recommended approach, what will be the cartridge product costs and margins?
-
Suppose sales in 2001 equal 26,000 unit, as in the budget constructed in January, and that actual manufacturing expenses turn out to equal budgeted expense. Prepare an income statement for the year (just include the manufacturing expense for expense) that will help senior management and the board understand the economics of cartridge production in 2001.
Anagene Inc Case Analysis
1. Describe Anagene’s competitive environment, including its industry, its specific customer base, its product / customer heterogeneity, and the major concerns facing Anagene
The market for Genomic analysis was not old enough in 2000 as the inception of the most of the companies took place in 1990s. At the same time, a large portion of the companies had yet to enter the market as their activities consisted of R&D and research. Even then, the Genomics instruments market was competitive and mature. Among its competitors, Anagene maintained a peculiar or prominent position in the industry by providing its customers with the ‘unloaded’ or ‘blank’ micro-arrays. This step gave the researchers the autonomy to test any type of sample. Meanwhile, these types of micro-arrays were also completely accurate. At the start of 2000, the majority of the customer base of the company consisted of those individual or institutional researchers who wanted to ascertain the quality of the micro-arrays. The most critical concern for Anagene relates to the notion of smoothing out the gross margins and costs. As the company was still in the process of developing and testing new equipments, the sales, margin and profit were highly volatile across quarters.
2. Considering your answer to item 1, is it likely that the existing cost system may adversely and significantly affect decisions to emphasize certain products or affect profit?
The existing cost system of Anagene allocates the costs to the products based on the budgeted sales or revenues. This sort of costing system has a peculiar flaw or disadvantage. If the budgeted level of activity goes down, the cost of the products increase dramatically. Consequently, the margins and the profits of the company are adversely affected. Currently, the company has two types of sales originating from its product base, the sales of cartridges and the sale of instruments. With the currently volatile costs of the cartridges, it is certain that the sales of the Genomics instruments (other than cartridges) are automatically emphasized. Moreover, if cartridges are removed from the income statement, then the critical figures (sales and profits) can be smoothed out.
3. What has caused the fluctuating margins for Anagene’s cartridges?
There are various reasons for the fluctuating margins of Anagene. The first reason associates itself with the prevalent costing methods of Anagene. Anagene calculates the costs and profits using the budgeted volume of the sales. Anagene is still in the process of becoming a fully mature company (in regards to products and services); therefore, both the budgeted and the actual level of activity are highly dubious and vague. The uncertain sales figure causes the margin to increase or decrease sharply. Secondly, as mentioned earlier, Anagene is still in the process of formulation of new products (cartridges). The new products do require some additional testing procedures. Anagene believes in the quality of its provided instruments; therefore, the testing process costs Anagene a considerable amount. This causes the cost to change dramatically. As these new products are demanded by customers at irregular intervals; therefore, the unplanned ‘testing costs’ appear in the income statement at asymmetrical intervals. This causes the costs and the margin to change intensely at intervals. Another reason for the fluctuating margins in the reuse of the cartridges by the users. The reuse does not allow analysts to ascertain the level of sales in the coming quarters. Moreover, it is very difficult to spot the emergence of new customers or a decline in the existing customers.
4. Should Kelly even be concerned with the assignment of overhead costs to cartridges and gross margins that include allocated overhead? Why not use variable contribution margin (selling price less variable costs, primarily materials) for management decision-making and reporting?
The inclusion of the overhead costs is very crucial for Kelly. The enclosure of overhead costs takes into account the idle capacity. However, the usage of the budgeted level of activity in the cost structure can possibly hide the idle capacity of Anagene. However, if the budget is formulated using the practical capacity than the overhead costs will be more meaningful as they will shed light on the idle capacity. Hence, overhead costs cannot be ignored as they affect the margin and profit. On the other hand, the contribution margin method of costing does not consider the fixed costs of Anagene. Hence, variable contribution margin will not be a suitable for reporting as the management will not acquire full information about the costs and processes. Anagene is expected to deal in emerging markets and inclusion of fixed costs is crucial. Moreover, as the fixed costs comprise a handsome portion of the overall costs; therefore, ignoring them will affect the profitability of the company. Moreover, the contribution margin method does not allow the management to discover the possibility of bottlenecks in the production process. Hence, variable contribution method is rather not an opposite pricing strategy.
Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Get Instant Access to This Case Solution for Only $19
Standard Price
$25
Save $6 on your purchase
-$6
Amount to Pay
$19
Different Requirements? Order a Custom Solution
Calculate the Price
Related Case Solutions
Get More Out of This
Our essay writing services are the best in the world. If you are in search of a professional essay writer, place your order on our website.