Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
The Takeover of The Norton Company Case Solution
BRT is contemplating an acquisition of the Norton Company. Norton has a strong competitive position, but mismanagement has led to inefficiencies, resulting in lackluster performance over the past decade. BRT has a detailed strategy for selecting potential acquisition targets. While Norton satisfies some of the features of the strategy, it is not clear if some other strategic objectives will be met. Norton has attracted the attention of some other potential acquirers as well. Coupled with the hostile attitude of management toward acquirers, competition from potential acquirers might force BRT to post a high acquisition offer for Norton. A variety of valuation methods have been used to determine the bid price for the target company. It is advised that BRT should post a higher bid than the current market price of Norton, but the bid should not be too high because BRT might not be able to fully implement the projected improvements.
Following questions are answered in this case study solution
-
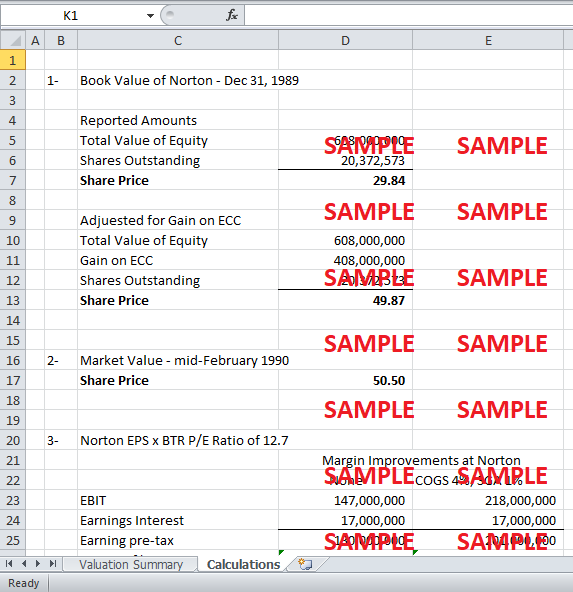
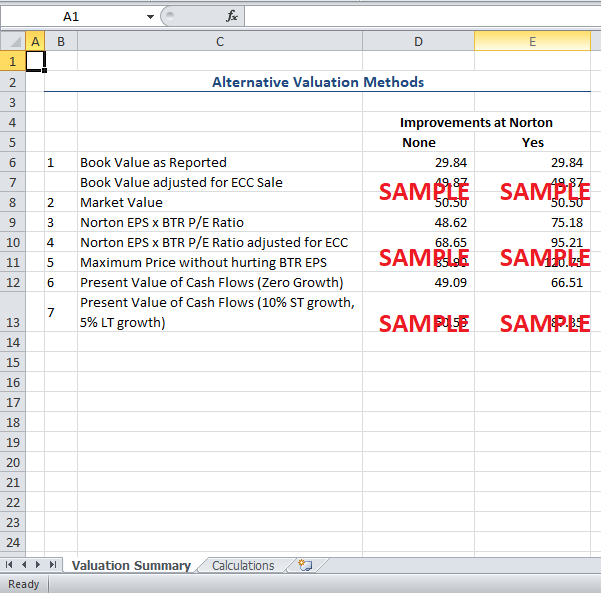
On spreadsheets using active cells wherever needed, reproduce all 7 alternative valuation numbers from the last three pages of the packet.
-
Evaluate Norton Co. as a takeover target by BTR plc relative to BTR’s strategy as formulated in the mid-1960s.
-
Owen Green, Chairman of BTR “anticipated that Norton would fetch full price.” Discuss why this was so.
-
In light of the valuation estimates of Norton in the last three pages of the packet, how should BTR formulate / evaluate the magnitude and financing of its bid for Norton Co.
Case Analysis for The Takeover of The Norton Company
1. On spreadsheets using active cells wherever needed, reproduce all seven alternative valuation numbers from the last three pages of the packet.
The seven alternative valuations have been reproduced in the attached spreadsheet. It should be noted that the spreadsheet calculations might be slightly different from the actual calculations due to rounding errors.
2. Evaluate Norton Co. as a takeover target by BTR plc relative to BTR’s strategy as formulated in the mid-1960s.
BTR had an elaborate strategy that they used to select potential acquisition targets. The success of the strategy could be ascertained from the success with which the company has been able to grow through acquisitions. The strategy was divided into five logical features that can be used to judge each target company. The first feature was to look for a target that was dominant in its market position and was adequately managed. While Norton enjoyed a strong competitive position, the company had produced inadequate financial results over the past decade – possibly due to poor management. However, BTR believed that it could improve the profit margins by implementing cost cutting and reducing excess capacity. The potential for increased efficiency and cost-cutting possibilities was in harmony with the second feature of BTR’s strategy – restructure the consolidated operations and remove inefficiencies. The third aspect of the strategy was to invest in equipment and research & development to maintain the competitive landscape of the company. BTR projected that it could improve the growth rate of Norton after acquisition, and it also projected to save $15 million a year of research and developments expenses for the next five or six years.
While the first three aspects of the strategy supported the acquisition of Norton, the last two features did not favor the target company. The fourth feature was to allow the target company’s management to retain control of the company. The possible rationale behind the strategy was that the subsidiary’s management knew the company well and could better manage the company in accordance with the objectives of the holding company. However, the current management of Norton was not favoring any acquisition offer. There was a good possibility that BRT would have to make a hostile bid without the support of management. Under such circumstances, BRT may not be able to (and may not even want to) retain the current management of Norton if the bid is successful. The last feature of the strategy is to use the cash flows generated by the acquired company to make further acquisitions. BRT expects to pay the ‘full price’ for Norton due to the hostile nature of the bid and the interest of other potential acquirers. Thereby, the acquisition may not be attractive, especially if BRT is not able to implement the cost-cutting measures adequately and improve the profit margins. Under such a scenario, the cash flow generated by Norton, after paying for debt used to finance the acquisition, may not be sufficient to support any further acquisitions.
While the target company supports some of the tenets of BRT’s strategy, the acquisition involves are certain degree of risk that prevent the Norton from being an ideal strategic fit. Norton may still prove to be a worthy acquisition, but BRT should be aware of the risks involved.
3. Owen Green, Chairman of BTR “anticipated that Norton would fetch full price.” Discuss why this was so.
While the financial condition of the company necessitated ac acquisition, the management of Norton was not too keen to sell the company. The meager stock performance of the company might compel the shareholders to accept an acquisition offer, but the management was likely to oppose any such offer. If BRT made an acquisition offer to the shareholders, the management would possibly advocate that the company could be worth more than the bid. Therefore, the bid price had to be high enough to convince the shareholders to ignore the advice of the management.
Moreover, three other companies had also shown interest in acquiring Norton. While none of these potential acquirers possessed a strategic fit with Norton, it was possible that they would out-bid BRT if BRT offered to pay less than the full price for the target. The situation was particularly precarious due to the presence of a French company as a potential acquirer. In a bid to dominate the industrial growth experienced by Germany, the French government had been encouraging its companies to acquire manufacturing firms from overseas. In this regard, the government was also encouraging financial institutions (banks) to provide financing for such acquisitions. These incentives, coupled with the perception of a strong local currency, motivated the French company to potentially post a high bid for the acquisition of Norton. In order to mitigate the risk of being out-bid, it was vital for BRT to post an attractive offer.
Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Get Instant Access to This Case Solution for Only $19
Standard Price
$25
Save $6 on your purchase
-$6
Amount to Pay
$19
Different Requirements? Order a Custom Solution
Calculate the Price
Related Case Solutions
Get More Out of This
Our essay writing services are the best in the world. If you are in search of a professional essay writer, place your order on our website.