Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
The Squeaky Horn Case Solution
The Squeaky Horn is a musical instrument repair shop. It specializes in the repair and restoration of both band and orchestral instruments. The shop is owned by Eugene Decker and his two partners. Recently, the shop has been losing its customers to Best Instrument repair, a new shop across town, due to higher prices. To attract and retain customers, Decker and his partners decided to lower the prices of minor repairs. This move led to a drastic decrease in profits as compared to the planned budget prepared earlier the same year. An analysis of the difference in the actual and budgeted statement shows that a rise in various costs, the hours required for a job and the change in quantity of jobs were responsible for the high difference in both profits.
Following questions are answered in this case study solution
-
Conceptually, what specific factors are likely to explain the difference between planned and actual results for the Squeaky Horn?
-
Prepare a revised budget with all prior planning assumptions retained, but use the total actual number of jobs the Squeaky Horn worked on (i.e., 4,405).
-
Prepare a profit reconciliation of planned versus actual profit by quantifying, in dollar terms, all significant contributing factors. (Hint: What did you identify in question 1?)
-
How do the different compensation arrangements at the Squeaky Horn impact profits?
-
What changes should Decker and his partners make based on the results of your analysis?
Case Analysis for The Squeaky Horn
1. Conceptually, what specific factors are likely to explain the difference between planned and actual results for the Squeaky Horn?
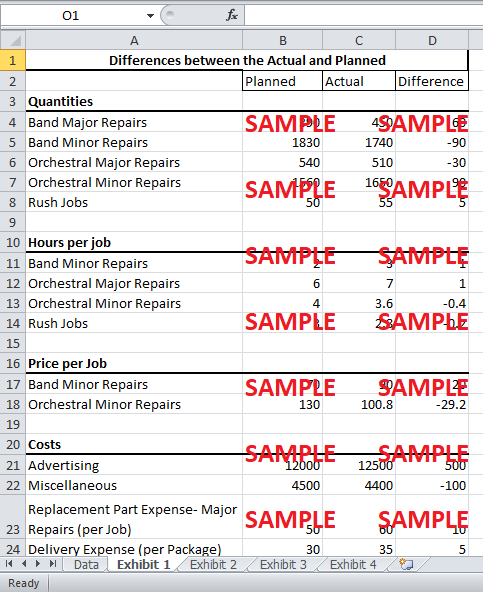
The Squeaky Horn is facing a problem due to the increase in competition as the technological advances lower the barrier to entry. This damaged the dominant role of the business. The competitor lowered costs to increase revenue. Hence, conceptually, change in revenue would seem like a major reason for the difference, given the situation the business is in. However, the actual revenue of the business has been $7,770 higher than the planned revenue. Therefore, it is important to look at factors that explain the difference between the results of the planned and actual results for Squeaky Horns. Exhibit 1 shows all the factors responsible for the discrepancy.
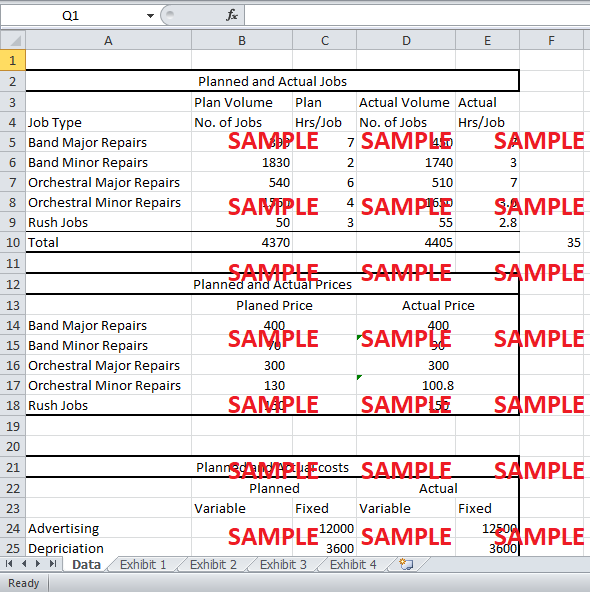
Firstly, the number of jobs budgeted were 35 jobs less than the actual number of Jobs. The number of band major repair and orchestral minor repairs were significantly more than expected. Similarly, the number of jobs for band minor repair and for orchestral major repair was lower from planned by 90 and 30 jobs, respectively. The rush jobs were also greater than expected by 5 jobs. This deviation from planned caused a major change in revenue as higher priced jobs increased.
Secondly, the actual time taken per job has also been different from the planned time. Band minor repairs and orchestral major repairs took 1 hour more than expected. Similarly, Orchestral Minor repair and rush jobs took slightly less time than expected. This would affect the variable cost as well as the revenue from the jobs.
Another reason for the difference can be the change in the pricing of band minor repair and orchestral minor repair. The Squeaky horns reduced the price of band major repair by $5 per hour and of orchestral minor repair by $4.5 per hour. This caused the per job price for band major repair to fall by $10 and for the orchestral minor repair to fall by $18.
The last major reason for the difference in budgeted and actual profits was the changes in the variable and fixed costs. The Replacement cost of major repairs per job increased by $10 and the shipping cost per package increased by $5. This cost increase as well as changes in number of jobs, caused the replacement part cost and the delivery cost to increase by $11,150 and $8,076, respectively (Exhibit 2).
The fixed cost also changed. The advertising cost rose by $500. The miscellaneous cost fell by $100. All these above changes would have caused the difference in profits.
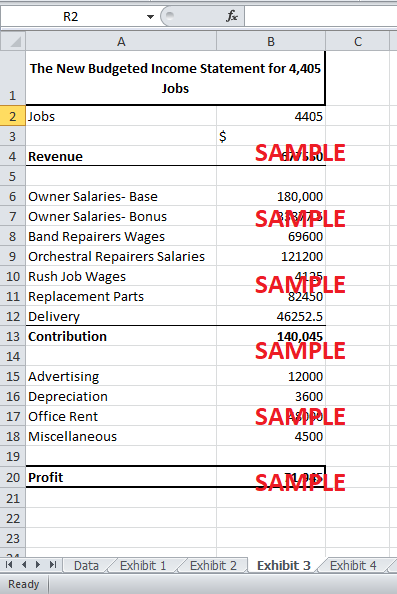
2. Prepare a revised budget with all prior planning assumptions retained, but use the total actual number of jobs the Squeaky Horn worked on (i.e., 4,405).
The planned statement prepared at the start of the year was based on the predicted jobs for each repair. The total number of jobs predicted was 4,370. However, during the year, the actual number of jobs totaled to 4,405 jobs. Therefore, a revised budget had to be made based on the actual number in order to analyze the actual difference in profits between the actual and the planned profits.
Exhibit 3 shows the revised budget after retaining all the prior assumptions but changing the number of jobs to the actual number. The fixed costs remain the same as before. However, the change in the number of jobs has caused the variable costs and revenues to increase. With the actual number of jobs and the historical cost, the profit should be $21,150 higher than the previous planned budget. All the variable costs rise, as well. Therefore, the contribution margin rises by $14,200 in the new budget. The revised budget shows a profit of $71,945.
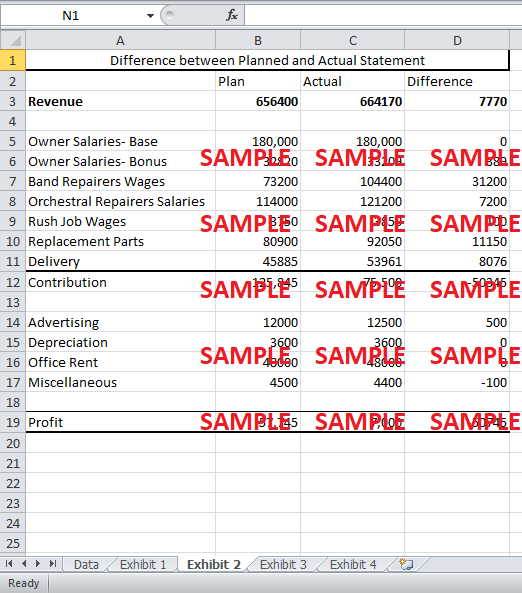
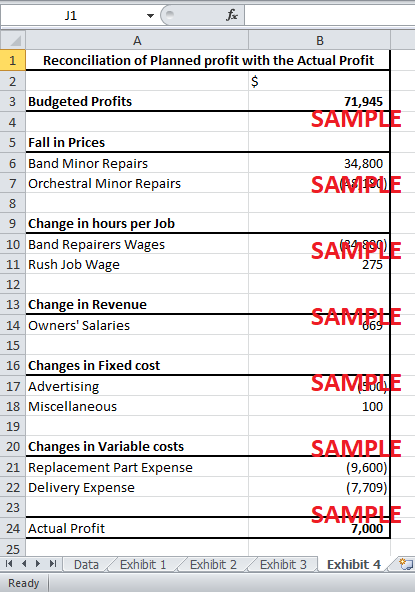
3. Prepare a profit reconciliation of planned versus actual profit by quantifying, in dollar terms, all significant contributing factors. (Hint: What did you identify in question 1?)
The profit of 71,945 has to be reconciled to an actual profit of $7,000. Exhibit 4 shows the statement of reconciliation of budgeted profit with the actual profit. The statement shows that the reduced revenue was due to the changes in prices. The reduced revenue also caused the owners’ bonus salary to fall by $669. Furthermore, the planned time taken per job increased by one hour for the band repairs. This caused an increase in the band repairer wages by $34,800. The time taken per job for the rush hour jobs decreased to 2.8 which reduced the rush job wage by $275. The changes in the fixed cost caused an increase by $500 in advertising expenses and a decrease by $100 in miscellaneous expenses.
Finally, there was an increase of $10 on the replacement part per job and of $5 on the shipment cost per package. The overall replacement cost was $9,600 more than the budgeted. Similarly, the overall delivery cost was $7,709 greater than the planned cost. Due to these changes in costs of replacement parts and delivery, the variable cost rose by $17,309.
Get instant access to this case solution for only $19
Get Instant Access to This Case Solution for Only $19
Standard Price
$25
Save $6 on your purchase
-$6
Amount to Pay
$19
Different Requirements? Order a Custom Solution
Calculate the Price
Related Case Solutions
Get More Out of This
Our essay writing services are the best in the world. If you are in search of a professional essay writer, place your order on our website.